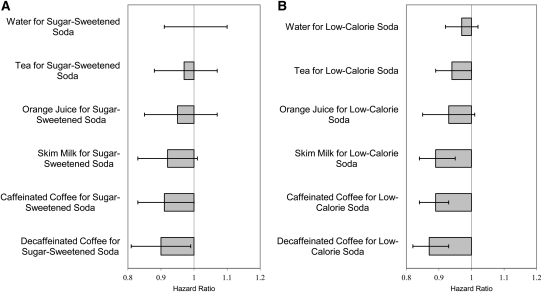
FIGURE 1.
Pooled RRs and 95% CIs associated with substitution of alternative beverages for sugar-sweetened soda (A) and low-calorie soda (B) among 43,371 men and 84,085 women (1 serving/d). RRs and variances for each substitution from each cohort were derived from a Cox proportional hazards multivariate model and then pooled in a fixed-effects model to arrive at a summary estimate of the effect of substituting one beverage for another in relation to total stroke risk; the Q statistic P value for between-study heterogeneity (null hypothesis is that there is no heterogeneity between Health Professionals Follow-Up Study and Nurses’ Health Study) for estimate of effect of substitutions is >0.05.