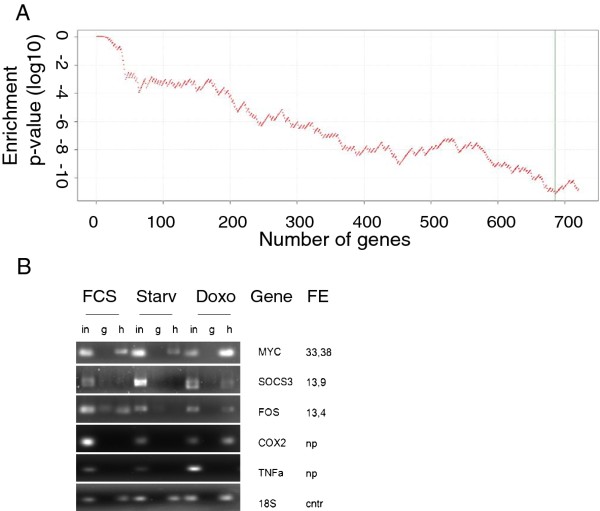
Figure 5.
A: Overepresentation analysis of ARE motif in 3'UTR of HuR bound mRNAs. The occurrence of AU rich elements (ARE) was annotated on the 3'UTR of all human genes using Transterm. Enrichment analysis of ARE motifs was carried out with a modified Fisher test on the HuR bound genes against the human genome as background. The 721 genes showing significant and specific fold enrichment upon HuR RIP-Chip were sorted in descending order according to their fold enrichment value. For each n from 1 to 721, the first n genes were considered in the enrichment analysis and the corresponding enrichment p-value was calculated and shown in the figure, where the x-axis represents the number of considered genes n, while the y-axis represents the log10 enrichment p-value corresponding to n. The maximum enrichment significance is reached with n = 683, as marked in the figure by a green vertical line. B: Experimental validation of RIP-Chip. Semiquantitative RT-PCR on RIP samples immunoprecipitated with anti-HuR antibody (h), whole serum IgG as a negative control (g) and the immunoprecipitation input (in). RIP analysis was performed on MCF-7 cells grown in standard condition (FCS), starved for 24 h (starved) or treated with doxorubicin 10 μM after starvation. Primers to detect mRNAs that showed an high fold enrichment score (MYC, SOCS3, FOS) during RIP-Chip analysis were chosen to test the quality of the microarray read out. Primers to detect COX2 and TNFa are literature reported HuR binding mRNAs and the 18S is a loading and immunoprecipitation control.