Figure 2.
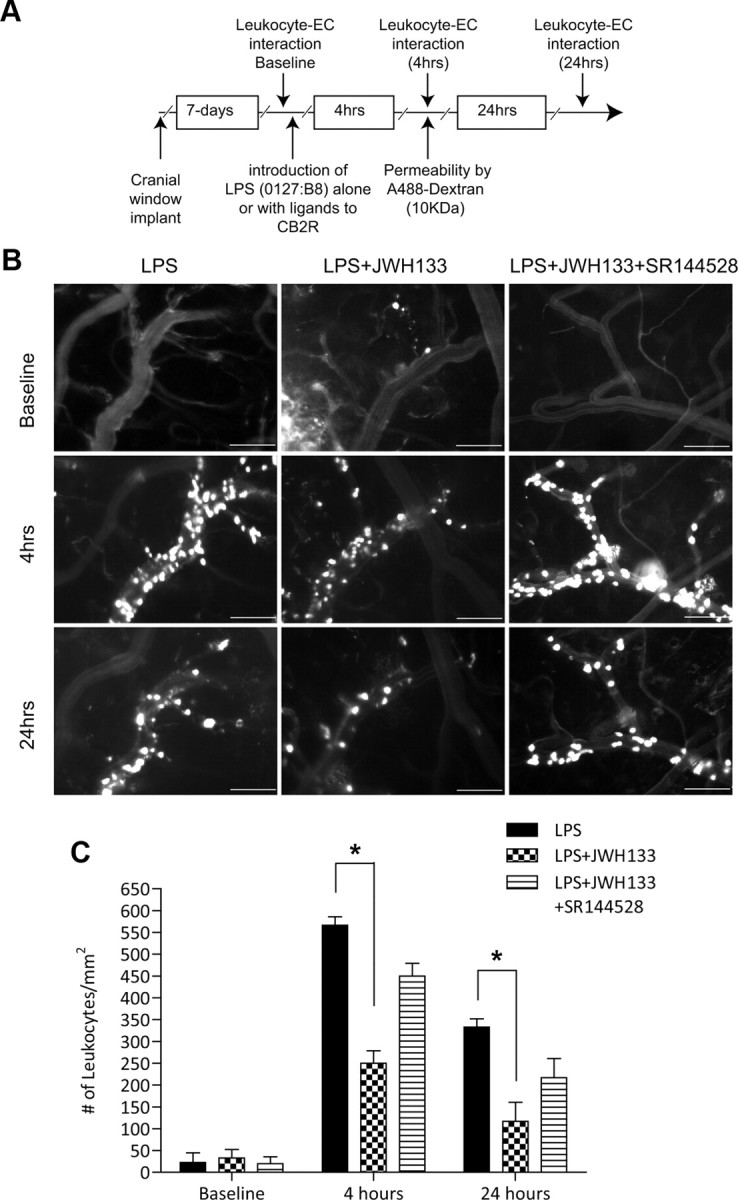
CB2R agonist reduces leukocyte adhesion in LPS-associated encephalitis. A, Experimental flow schematic of treatments and intravital microscopy endpoints. C57BL/6 mice were implanted with cranial windows as described in Materials and Methods. B, Seven days after the cranial window procedure, animals were placed in the following experimental conditions: LPS alone (6 mg/kg, i.p.), LPS with CB2 agonist JWH133 (10 mg/ml, i.p.), and LPS with JWH133 and the CB2R antagonist SR144528 (10 mg/ml, i.p.). Representative images from a video of leukocytes labeled with the fluorescent compound rhodamine 6G were visualized for adhesion in pial venules at 0, 4, and 24 h by intravital microscopy. The top row shows the baseline leukocyte adhesion. The middle and bottom rows represent images taken at 4 and 24 h, respectively. Scale bars: 100 μm. C, Quantitative measurements of leukocytes under firm adhesion (not rolling) during an observation period of 30 s. Adhering leukocytes from multiple vessels and from at least three fields of view per animal (three animals per group) were scored as the number of cells per square millimeter of the vascular surface area, calculated from the diameter and standardized length (100 μm) of the vessel segment under investigation. The results are shown as the mean adhesion ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.001 [difference between the groups compared (brackets)].
