Figure 3. Effect of C1 in HeLa cells.
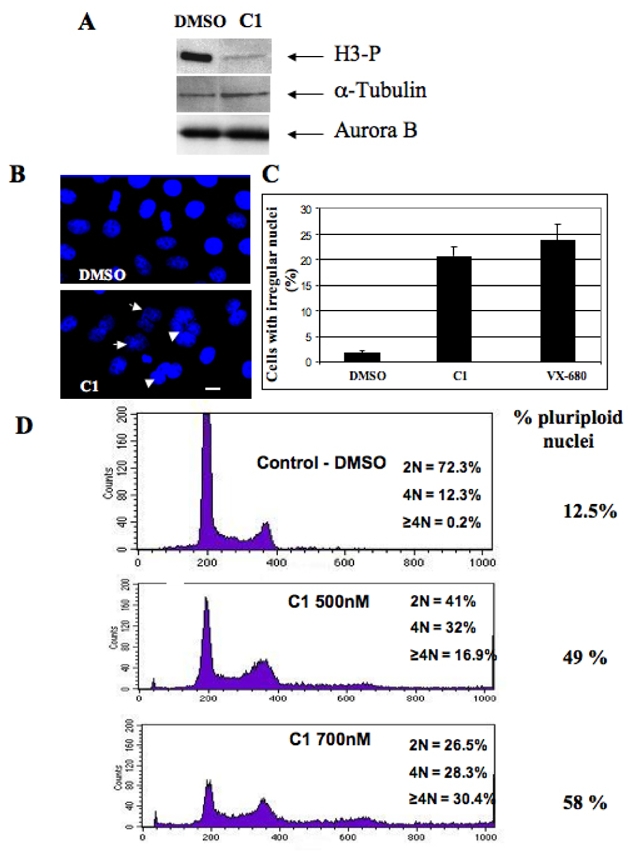
(A) Western blot analysis of histone H3 phosphorylation. HeLa cells were incubated overnight with Nocodazole (50 nM) in the presence of either DMSO or C1 (2 μM). Cells were then collected and lysed. Identical amounts of the lysed cell samples were run on 18% acrylamide gel containing SDS. After transfer, the blot was revealed using an antibody against phosphorylated histone H3. The same membrane was also revealed using antibodies against α-tubulin and Aurora B for estimation of both the amount of loaded proteins and of mitotic cells, respectively.
(B) Treatment with C1 resulted in perturbation of the structure of the cell nuclei. HeLa cells were incubated overnight in the presence of either C1 (2 μM) or DMSO (1%). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33 342 and visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Arrows indicate irregular nuclei. Similar perturbations in the nuclear structure were obtained upon treatment with 300 nM VX-680 (not shown). Bar, 5 microns.
(C) Quantification of the data presented in (B). The percentage of irregular (lobed and polyploid) nuclei was determined in two independent experiments; 100 cells were analyzed per experiment.
(D) FACS analysis shows that treatment with C1 results in a dramatic increase of the amount of polyploid cells. The experiments were performed with control HeLa cells (incubated only in the presence of 1% DMSO) and HeLa cells incubated with C1 (at either 500 nM or 700 nM) for 48 hours. DNA was stained with propidium iodine and the samples were analyzed by using a Beckton-Dickinson FACS analyzer. The percentage of polyploid cells (cells with a ploidy ≥2N) is indicated on the right part of the figure.
