Figure 6. Nuclear displacement induced defects in CAR formation and cytokinesis failure in tea4Δ andpom1Δ cells.
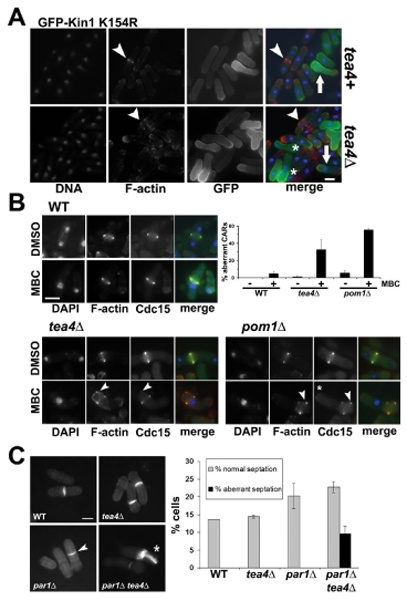
(A) Overexpression of kinase dead (GFP-Kin1 K154R) Kin1 versions in tea4+ or tea4Δ cells. After growth overnight at 30°C in the absence of thiamine (ON) in the culture medium, cells have been fixed and stained with DAPI (DNA, blue) and rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin (F-actin, red). Fluorescent signals and superposition of images are shown (merge). Arrowheads show normal (tea4+) or aberrant (tea4Δ) CARs and arrows indicate the displaced nuclei towards the cell end where GFP-Kin1 K154R accumulates. (B) Cdc15-GFP, tea4Δ cdc15-GFP and pom1Δ cdc15-GFP cells were treated for 2h with 50 μg/ml MBC or 1% DMSO as a control. Cells have been fixed and stained with DAPI (DNA, blue) and rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin (F-actin, red). Fluorescent signals and superposition of images are shown (merge). Arrowheads show abnormal F-actin structures or Cdc15-GFP dots outside the CARs and asterisks show cell end localized Cdc15-GFP. A histogram shows the percentage of aberrant CARs with both F-actin and Cdc15-GFP incorporation defects in the different strains with (+) or without (-) MBC. (C) Wild type (WT), tea4Δ, par1Δ and tea4Δ par1Δ cells have been grown at 30°C and stained with methyl blue. Arrowhead indicates a misplaced septum and asterisk shows an aberrant septation, histogram on the right shows the percentage of normal and aberrant septations in WT, tea4Δ, par1Δ and par1Δ tea4Δ cells (n>200 total cells, in duplicate). Bars: 5 μm.
