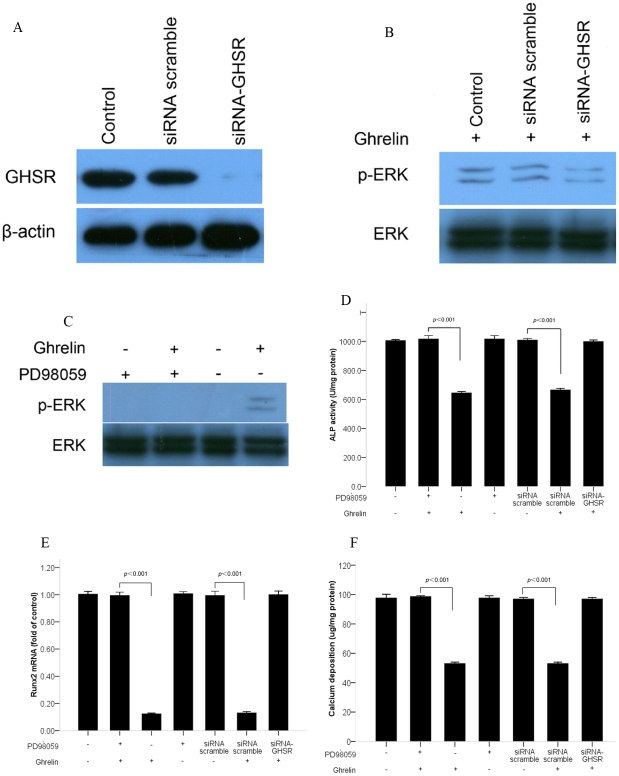
Figure 4. ERK signaling pathway mediated the inhibitory effect of ghrelin on osteoblastic differentiation of calcifying vascular smooth muscle cells (CVSMCs).
(A) The expression and silencing of growth hormone secretagog receptor (GHSR) on CVSMCs. Cells were incubated with scramble siRNA or GHSR siRNA for 72 h. Total cellular protein was subjected to western blot analysis using anti-GHSR antibody. The anti-GHSR antibody identified a band at 44 kDa. β-actin was used as the control. (B) The activation of extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) under the silencing of GHSR. Cells were incubated with scramble siRNA or GHSR siRNA for 72 h prior to treatment with 10−6 mol/L ghrelin for 30 min. Total proteins were subjected to western blotting and incubated with antibody against p-ERK and ERK. The representative results are shown. (C) The activation of ERK under PD98059. Cells were incubated with PD98059 (10 µM) for 2 h prior to treatment with 10−6 mol/L of ghrelin for 30 min. Total proteins were subjected to western blotting and incubated with antibody against p-ERK and ERK. The representative results are shown. (D, E, F) The decreased alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, Runx2 mRNA, and calcium deposition mediated by the GHSR/ERK pathway. Cells were incubated with PD98059 (10 µM) for 2 h prior to treatment with 10−6 mol/L of ghrelin. Cells were also treated with the scramble siRNA or GHSR siRNA in the presence of 10−6 mol/L of ghrelin. ALP activity, Rnux2 mRNA, and calcium deposition were measured. The bars represent the mean ±standard deviation (SD) (n = 3).