Figure 1. LVs dephosphorylate LPS and interact with native lumenal bacteria.
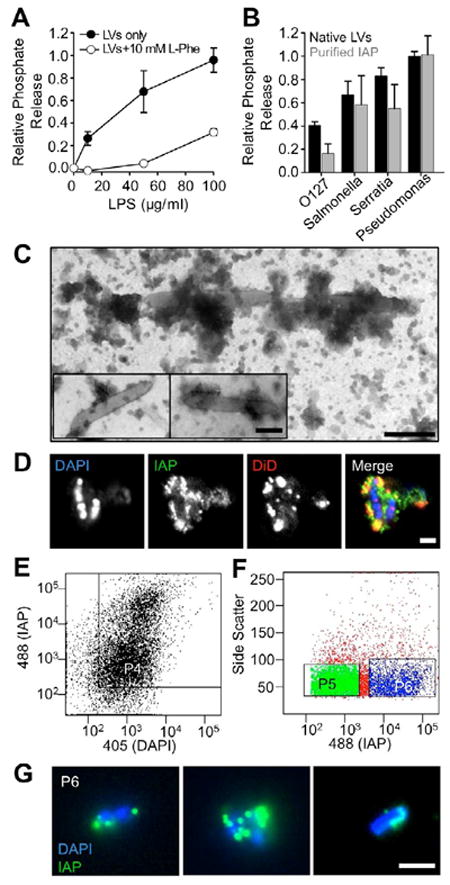
(A) LVs release phosphate from E. coli O55:B5 LPS in a concentration dependent manner; phosphate release is reduced by the IAP competitive inhibitor L-phenylalanine (L-Phe). (B) LVs (200 μg LVs/ml) and purified IAP (2 U/ml) differentially dephosphorylate LPS derived from various Gram-negative bacterial species. Data represent mean ± SEM. (C) TEM imaging reveals vesicle-like particles in close association with native lumenal bacteria from rat LV preparations. Bar, 200 nm. (D) CM imaging reveals IAP enrichment (green) on membranes (red) associated with DAPI-stained bacteria (blue). Bars, 2 μm. (E) Pre-sort input material was analyzed for staining with both anti-IAP (LVs) and DAPI (bacteria) using the P4 gate. (F) P4 material was sorted using gates for IAP (P5, low IAP enrichment) and dual stained material (P6, high IAP enrichment). (G) CM images of sorted P6 material show native LV/microbe complexes (green = IAP, blue = DAPI). Bar, 2 μm.
