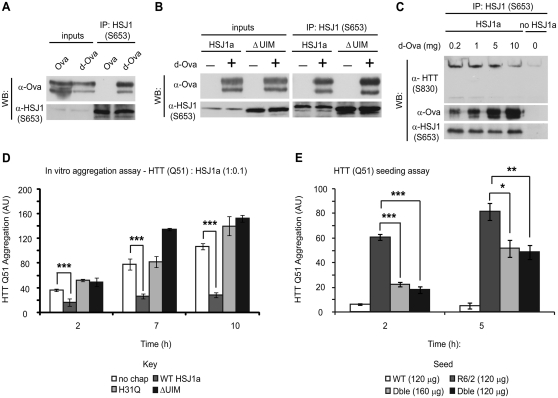
Figure 7.
HSJ1a reduces huntingtin aggregation in a J-domain and UIM-dependent manner. Purified wild-type (A and B) or ΔUIM (B) HSJ1a was incubated with native (Ova) or denatured ovalbumin (d-Ova) for 30 min at room temperature, after which, anti-HSJ1 antibody S653 was used to immunoprecipitate material from incubations. Western blotting was performed to determine levels of HSJ1a and ovalbumin after immunoprecipitation. (C) Lysates from SK-N-SH cells expressing HSJ1a were incubated with 15-week R6/2 brain lysates in the presence of 0.2, 1, 5 or 10 mg of denatured ovalbumin. Levels of denatured ovalbumin, huntingtin and HSJ1a were determined by immunoblotting after immunoprecipitation with anti-HSJ1 (S653). (D) GST-HTT Q51 in vitro aggregation assays were performed in the presence of SK-N-SH cell lysates and ATP regenerating system containing no additional chaperone (white bars), wild-type HSJ1a (dark grey bars), J-domain inactive HSJ1a (light grey bars) or ΔUIM HSJ1a (black bars). HSJ1a was added to GST-HTT Q51 at a ratio of 1:10. Reactions were stopped 2, 7 and 10 h after removal of GST tag from GST-HTT Q51 by TEV protease cleavage. Levels of detergent insoluble mutant huntingtin were determined by filter trap, immunoblotting and densitometry. Mean signal was plotted for each group ± SEM (n = 4). (E) GST-HTT Q51 in vitro nucleation assays were performed using 120 ng of detergent insoluble material purified from brains of wild-type (white bars), R6/2 (light grey bars) or double transgenic (black bars) or 160 ng from double transgenic (dark grey bars). Mean signal was plotted for each group ± SEM (n = 6). Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005).