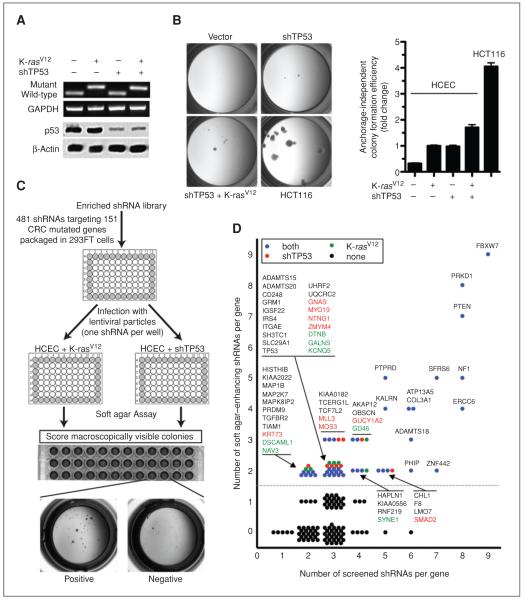
Figure 1.
Identification of tumor suppressors within CRC CAN-genes with an enriched shRNA library by using isogenic HCECs. A, total RNA from immortalized HCECs and their oncogenically progressed derivatives expressing K-rasV12, shTP53, or both were subjected to qRT-PCR followed by a diagnostic restriction digestion assay to detect WT and mutant KRAS alleles. Whole-cell extracts from same cells were immunoblotted for expression of p53. B, each cell line was cultured in soft agar in 96-well plates for 3 weeks and photographed with a stereomicroscope. Colonies larger than 0.1 mm in size are quantified. Bars represent 12 data points (3 separate experiments in quadruplicates), mean ± SEM. C, schematic representation of the strategy. HCECs expressing K-rasV12 or shRNA against p53 were infected with lentiviral shRNA constructs in “one-shRNA-one-well” format and the ability of cells to form macroscopic soft agar colonies was assessed after 3 weeks. D, scatter plot showing the overall results of the screens. Each circle represents a gene. Context-dependent anchorage-independent growth suppressors are shown in green (K-rasV12–specific hits) and red (shTP53-specific hits) whereas context-independent suppressors are shown in blue. All genes, except those isolated only in K-rasV12 context, were plotted according to results obtained from shTP53 context.