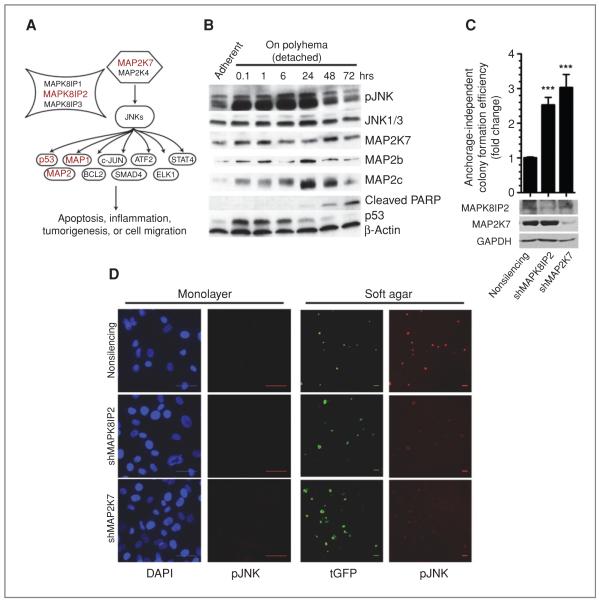
Figure 3.
Identification of JNK pathway as suppressor of anchorage-independent growth. A, schematic representation of JNK pathway. shRNAs against 5 members of this pathway (red) was found to enhance soft agar growth. B, whole-cell extracts from immortalized HCECs were immunoblotted for JNK pathway members in response to loss of attachment. C, fold change in soft agar colony formation efficiency in response to MAPK8IP2 or MAP2K7 depletion in shTP53-expressing HCECs. Bars represent 16 data points from 2 separate experiments, 2-tailed Student t test, mean ± SEM. ***, P < 0.0001. D, phosphorylated (active) JNK immunofluorescence staining of cells in (C), either in monolayer or soft agar culture. Bars: 50 μm, tGFP is encoded from the shRNA vector, 24 hours after seed. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.