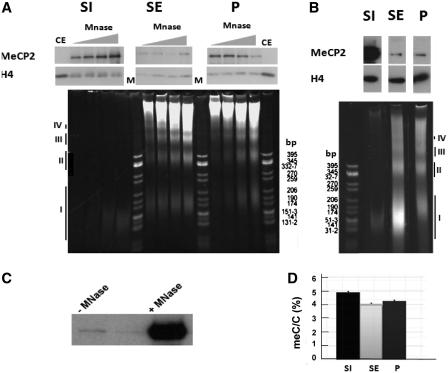
Figure 2.
Preferential fractionation of MeCP2 with the S1 fractionation depends on the extent of micrococcal nuclease digestion. (A) Time-course digestion of rat whole-brain nuclei with MNase at 10 U/mg of DNA for 2, 4, 8 and 12 min followed by fractionation to yield S1, SE and P. The upper panel shows a western blot for MeCP2 that is normalized for H4. Lower panel contains 4% native acrylamide gel of the DNA associated with the S1, SE and P. CE: chicken erythrocyte histones; M: pBR322—CfoI-digested marker. (B) Same as in (A), but using MNase at 30 U/mg of DNA for 15 min. The roman numerals (I–IV) in both (A) and (B) indicate the DNA fragments corresponding to mono-, di-, tri- and tetra-nucleosomes respectively. (C) Western blot analysis of MeCP2 released from brain nuclei without (–) and with (+) micrococcal nuclease digestion treatment reveals that essentially all nuclear MeCP2 is bound to chromatin. (D) HPLC-determined relative meC/C percentile of the fractions shown in (B).