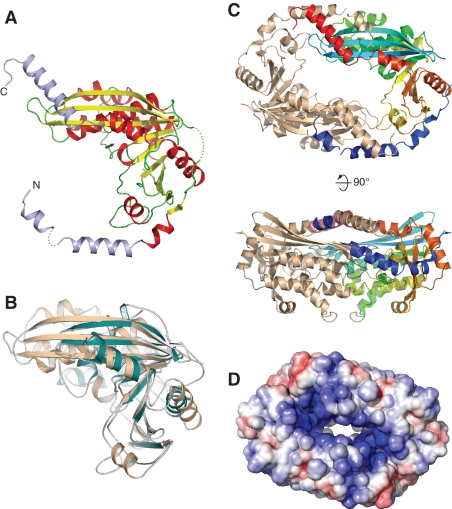
Figure 4.
Crystal structure of NurA. (A) NurA belongs to the RNAseH-like family of nucleases. The structure is shown as a ribbon, coloured according to secondary structure elements (alpha helices are red and beta sheets yellow). The N- and C-terminal helical extensions that are not part of the RNAseH fold are coloured in light blue. The position of the active site is indicated by an arrow. (B) Structural superposition of NurA and Endo V from T. maritima (PDB ID: 2w36). NurA is shown in light brown and Endo V in green. (C) Dimeric arrangement of NurA chains, as observed in the crystal. In the dimer, one protomer is coloured from the N- (blue) to the C-end (red), the other is coloured light brown. Two views are shown, related by a 90° rotation. (D) Electrostatic properties of the NurA protein. The electrostatic potential was calculated with APBS (32) and mapped onto the solvent-accessible surface of the structure, at contouring levels of ±5 kT (blue/red).