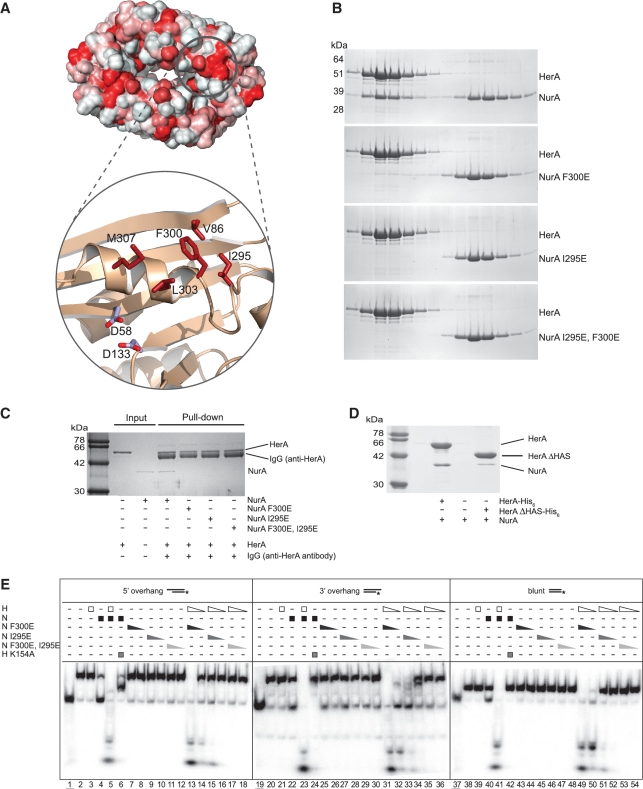
Figure 6.
Characterization of the HerA–NurA interaction. (A) Hydrophobic nature of the NurA surface, plotted red (most hydrophobic) to white (least hydrophobic) on the solvent-accessible surface of the protein. A hydrophobic patch formed by V86, I295, F300, L303 and M307 adjacent to the active site (marked by the side chains of D58 and D133) is shown in close-up view. (B) Gel-filtration analysis of the interaction between HerA and NurA and the NurA single mutants F300E, I295E and double mutant I295E, F300E. SDS–PAGE analysis of eluted fractions from a Superdex 200 HR 10/30 column. (C) Immunoprecipitations between HerA and NurA or the NurA F300E, NurA I295E or NurA I295E/F300E mutant proteins using HerA-specific polyclonal antibodies. Complexes were retrieved on protein-A sepharose beads, before separation by SDS–PAGE. (D) Pull-down analysis demonstrating the loss of interaction between NurA and HerA ΔHAS. 35 µg of HerA his-tagged HerA (0.10 nmol of hexamer) was mixed with 15 µg untagged NurA (0.19 nmol of dimer) at 60°C for 20 min. The complex was retrieved on nickel-agarose beads and eluted by boiling. (E) Helicase–nuclease assays using the radiolabelled substrates as described in Figure 1B demonstrating reduced nucleolytic activity in the HerA–NurA F300E, HerA–NurA I295E and HerA–NurA F300E/I295E mutant complexes. Triangles depict decreasing concentrations of proteins (450 nM and 45 nM HerA hexamer or NurA dimer). Lanes 1, 19 and 37 (underlined); boiled samples. Lanes 2, 20 and 38; no protein added. Lanes 3, 21 and 39; HerA. Lanes 4, 22 and 40; NurA. Lanes 5, 23 and 41; HerA–NurA complex. Lanes 6, 24 and 42; HerA K154A–NurA. Lanes 7–8, 25–26 and 43–44; NurA F300E. Lanes 9–10, 27–28 and 45–46; NurA I295E. Lanes 11–12, 29–30 and 47–48; NurA F300E/I295E. Lanes 13–14, 31–32 and 49–50; HerA–NurA F300E. Lanes 15–16, 33–34 and 51–52; HerA–NurA I295E. Lanes 17–18, 35–36 and 53–54; HerA–NurA F300E/I295E.