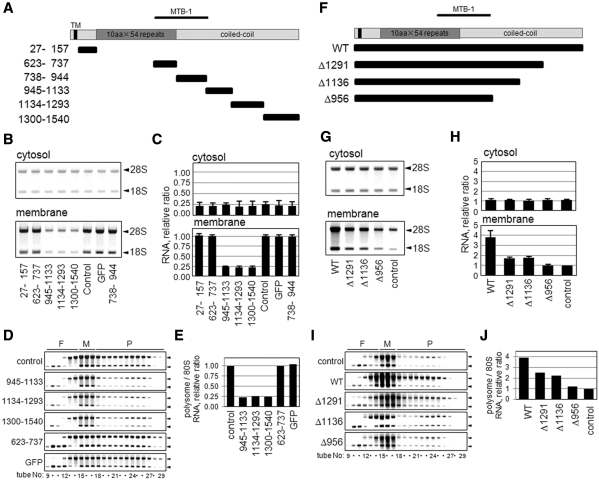
Figure 7.
Cytoplasmic expression of the coiled-coil domain perturbs polysome assembly on the membranes. (A) Schematic representations of full-length and truncated constructs of various regions of p180. Human p180 has a predicted transmembrane domain (TM) close to the N-terminus, a highly basic tandem repeat domain (dark gray box), a microtubule binding and bundling domain (MTB-1) and a C-terminal acidic coiled-coil domain (gray boxes). The numbers on the left of each truncated mutant denote the amino acid residues of human p180 (DDBJ accession number: AB287347). (B) A series of GFP-tagged polypeptides containing different regions of human p180 were expressed in HEL cells, and the rRNAs (indicated by 28S and 18S, respectively) in the cytosolic and membrane fractions are shown. (C) The RNA contents in the cytosolic and membrane-bound fractions were estimated by densitometric scanning, and the relative amounts are shown. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3). (D) Polysome analyses were performed using the membrane fractions of cells overexpressing peptides containing amino acid residues 945–1133, 1134–1293 and 1300–1540 compared with those of control cells or cells overexpressing control peptides. Arrowheads indicate 28S (upper) and 18S (lower) rRNAs. (E) The relative ratios of polysomal RNA to 80S RNA are shown. (F) Schematic representations of wild-type and various C-terminal deletion mutants of p180. (G) Expression plasmids encoding wild-type p180 and p180 mutants were transfected into HeLa cells. The rRNAs in the cytosolic and membrane fractions were analyzed. (H) The relative RNA contents in the cytosolic and membrane-bound fractions are shown. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3). (I) Polysome analyses were performed using the membrane fractions of these cells. Arrowheads indicate 28S (upper) and 18S (lower) rRNAs. (J) The relative ratios of polysomal RNA to 80S RNA are shown.