Figure 3.
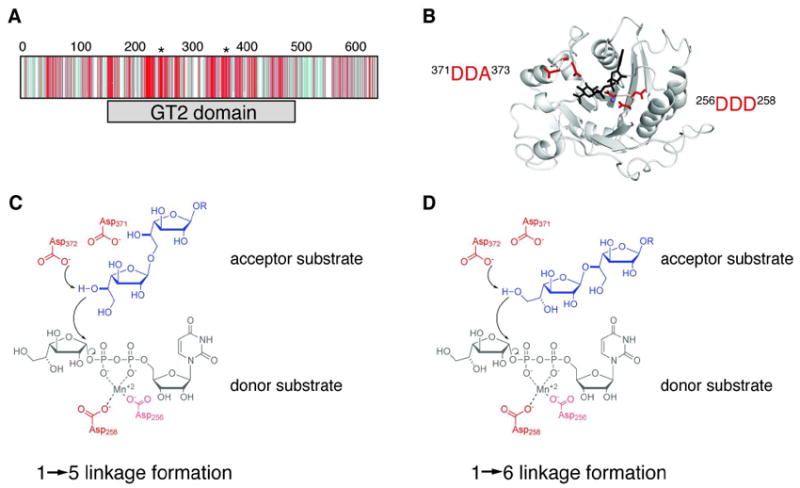
Identification of one putative active site in GlfT2. (A) Depiction of the CLUSTALW2-generated multiple sequence alignment of 50 homologs to GlfT2 shows that the conserved residues (shades of red) occur mostly within the GT-2 domain (gray bar), while divergent residues (shades of blue) occur mostly in the other regions of the protein. The positions of the two conserved DXD motifs are indicated with asterisks above the sequence alignment. (B) A homology model of the GT-2 domain of GlfT2 (residues 160-398) was computed from the structure of chondroitin polymerase from E. coli K4 (K4CP: PDB ID: 2Z86, subunit A). The DDA motif (red, left) and the DDD motif (red, right) are located in a putative active site near the donor substrate from K4CP, UDP-glucuronic acid (black) and the Mn2+ ion (purple sphere). (C, D) Chemical view of the hypothesized roles of the conserved motifs. The DDA motif is predicted to contain the catalytic base that deprotonates the nucelophilic hydroxyl on the acceptor to produce the Galf-β-(1→5)-Galf (C) or Galf-β-(1→6)-Galf (D) glycosidic linkage. The DDD motif is predicted to assist in binding the divalent cation.
