Figure 8.
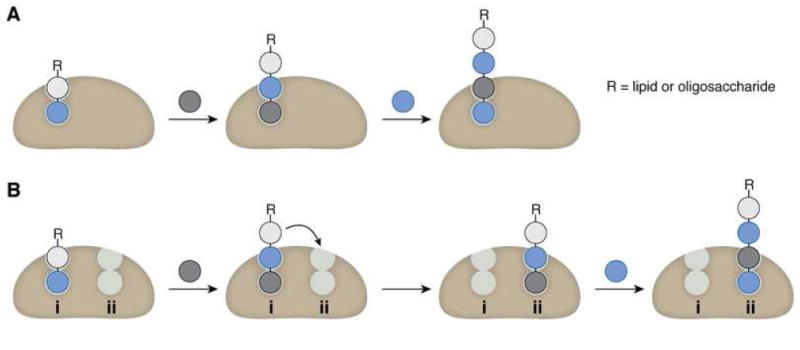
Comparison of one active site versus two active sites for processive synthesis of an alternating polymer. (A) The use of one multifunctional active site facilitates retention of the growing polymer by the polymerase through multiple catalytic additions. (B) The use of two active sites for processive synthesis requires translocation of the growing chain between each site, which adds complexity to the mechanism of elongation and may be disfavored by the principle of least motion.
