Figure 2.
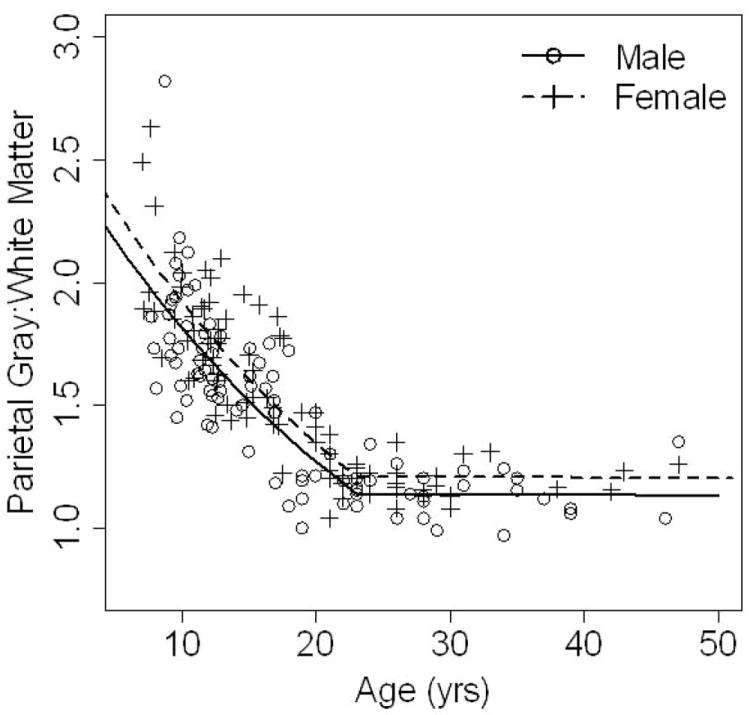
Mean parietal gray-to-white matter ratio is shown on the y axis, plotted against age on the x axis. Males (solid line) and females (dotted line) have the same rate of decline (there is no sex by age interaction) throughout the entire age span. In the younger ages, the change over time is quite rapid with a steep decline in ratio values. However, after age 23, the parietal gray-to-white matter ratio essentially stabilizes and comes to a plateau. The females (dotted line) have higher measures of parietal lobe gray-to-white matter ratios throughout the wide age range measured here (7-50 years).
