Figure 1.
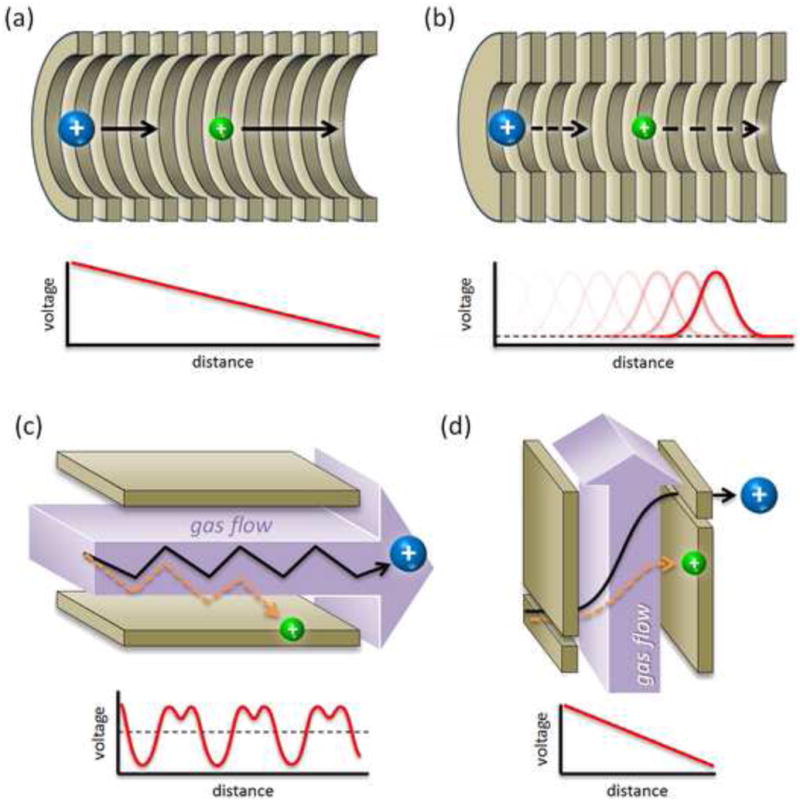
Basic operational principles of contemporary ion mobility techniques. (a) Conventional drift time ion mobility whereby ions are introduced into a gas-filled chamber and separated based upon their differential drift down a continuous declining potential. (b) Traveling wave ion mobility which mobility separates ions in a gas-filled chamber using a dynamic traveling potential hill. (c) Asymmetric field ion mobility whereby ions are separated based upon their differential migration orthogonal to a sweeping gas flow. (d) Differential ion mobility which separates ions based upon their ion mobility-dependent spatial displacement as they traverse an electric field gradient that is applied orthogonal to a constant flow of gas. In all schemes, ion motion is depicted from left to right.
