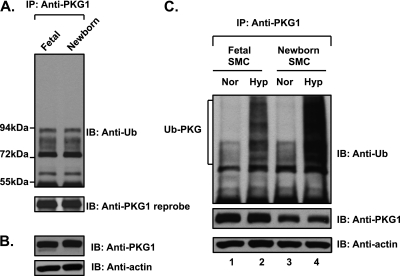
Figure 3.
Fetal and newborn pulmonary arteries do not demonstrate increased ubiquitin modification of PKG1. The ubiquitin modification of PKG1 is increased in both fetal and newborn pulmonary artery SMCs upon exposure to acute hypoxia. (A) Fetal arteries were isolated under hypoxic conditions as in utero. Ovine fetal and newborn pulmonary artery extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-PKG1 antibody and analyzed by Western blotting, using an anti-ubiquitin antibody. The blot was reprobed with anti-PKG1 antibody. (B) The arterial tissue extracts were analyzed by Western blotting, using anti-PKG1 and actin antibodies. (C) Fetal and newborn ovine pulmonary artery SMCs were exposed to hypoxia or normoxia for 3 hours. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with PKG1 antibody and assessed by Western blotting, using an anti-ubiquitin monoclonal antibody (top). Blots were reprobed with PKG1 antibody (middle). Actin in cell extracts served as loading control (bottom). A representative blot from three experiments is shown.