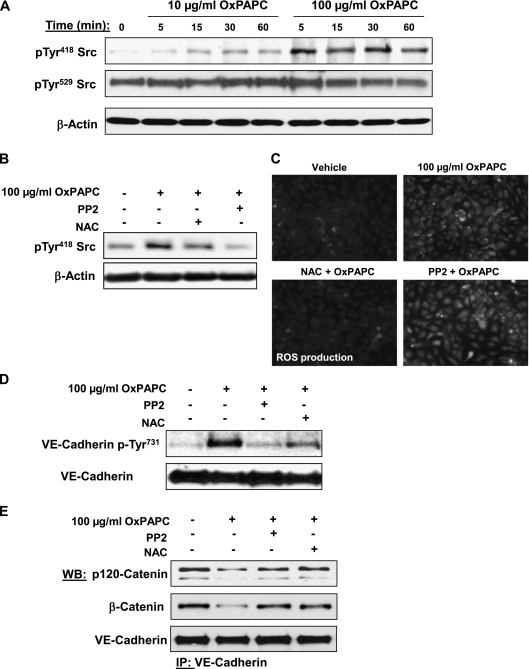
Figure 6.
Analysis of OxPAPC-induced Src phosphorylation and effects of Src and ROS inhibitors on VE-cadherin phosphorylation and the formation of VE-cadherin–p120-catenin–β-catenin complexes. (A) HPAECs were stimulated with OxPAPC (10 μg/ml or 100 μg/ml) for indicated periods of time, and Src phosphorylation at Tyr418 and Tyr529 was examined by Western blot analysis. Staining with β-actin antibody was used as a normalization control. (B–D) Cells pretreated with vehicle, Src inhibitor PP2 (1μM), or the antioxidant N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC; 1 mM) for 30 minutes were stimulated with OxPAPC (100 μg/ml, 15 minutes). Concentrations of Src phosphorylation at Tyr418 were detected by Western blot analysis. (B) Staining with β-actin antibody was used as a normalization control. (C) The assay of ROS production was performed as described in Materials and Methods. (D) Concentrations of VE-cadherin phosphorylated at Tyr731 were detected by Western blot analysis. (E) Cells pretreated with vehicle, PP2 (1 μM), or NAC (1 mM) for 30 minutes were stimulated with OxPAPC (100 μg/ml, 15 minutes), followed by immunoprecipitation with anti–VE-cadherin antibody. Coimmunoprecipiated p120-catenin and β-catenin were detected by Western blot analysis with corresponding antibodies. The detection of immunoprecipiated VE-cadherin was used as a normalization control. The results shown are representative of five independent experiments.