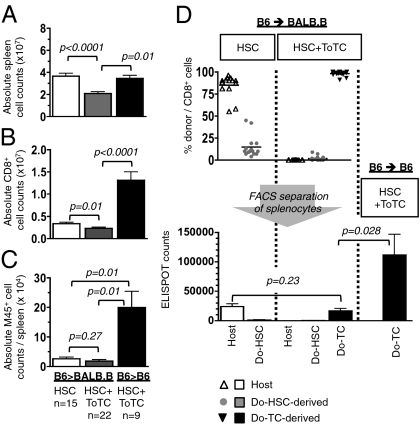
Fig. 1.
Early posttransplantation anti-MCMV response. BALB.B or B6 mice transplanted with B6 HSCs or HSC+ToTCs were infected 2 wk after HCT with a sublethal dose of 1 × 105 pfu MCMV RM427+. Tissues were harvested 2 wk postinfection. (A) BALB.B recipients of B6 HSC+ToTCs had significantly lower mean absolute cell numbers per spleen compared with BALB.B recipients of B6 HSCs or B6 recipients of B6 HSC+ToTCs. (B) BALB.B recipients of pure B6 HSCs or B6 recipients of B6 HSC+ToTCs had significantly higher absolute CD8+ cell numbers per spleen than BALB.B recipients of B6 HSC+ToTCs. (C) Absolute numbers of M45-tetramer+ splenocytes were equivalent in BALB.B recipients of B6 HSCs or HSC+ToTCs, but higher in B6 recipients given B6 HSC+ToTCs. (D) Separation of splenocytes by FACS into populations derived from host, donor HSCs, or transferred ToTCs, based on GFP expression or CD45 allele type. BALB.B recipients of B6 HSCs were mixed CD8+-chimeras (host exceeding donor). No residual host, few donor HSC-derived, and mainly cotransferred donor CD8+ cells were detectable in BALB.B recipients of B6 HSC+ToTCs (Upper). Antiviral IFN-γ responses to MCMV peptide, assessed by ELISPOT, revealed better responses from residual host CD8+ populations in B6 HSC recipients vs. transferred donor T cells in B6 HSC+ToTC recipients. Shown for comparison is the robust response of B6 donor T cells coinfused into B6 recipients.