Figure 7.
Effect of Distance between Acetylated Lysines and In Vivo Binding of BRD4
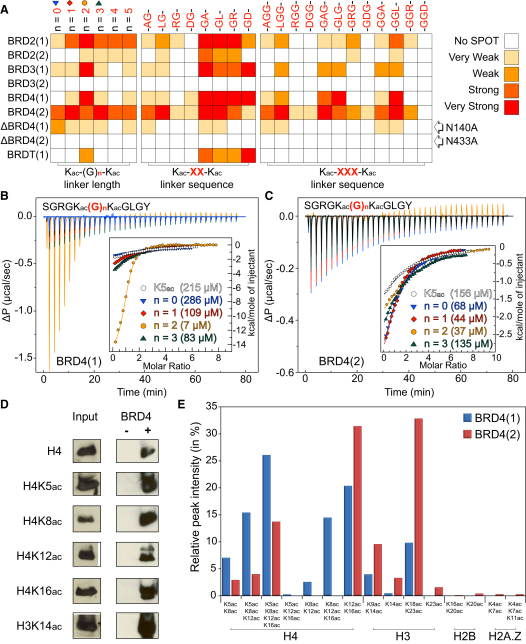
(A) Effect of poly-Gly and linker sequence on binding of doubly acetylated peptides to BET BRDs profiled by SPOT assays. Interactions are weakened or abolished when the docking asparagine is mutated to an Ala (N140A for the first and N433A for the second BRDs of BRD4).
(B) Effect of poly-Gly linker on the binding of H4K5acK8ac to BRD4(1) evaluated by ITC, demonstrating that the natural recognition sequence has the optimal sequence for binding. Peptide sequences are given in the inset.
(C) The second BRD of BRD4 is more promiscuous as demonstrated by ITC, exhibiting weaker binding for all tested peptides.
(D) Immunoprecipitation of Flag-tagged BRD4 from transfected cell nucleosome fraction and western blotting using anti-acetylated histone antibodies. Input represents 1% of total input. IgG was used for control immunoprecipitations.
(E) Individual BRD4 BRDs purify histones with distinct acetylation status from histone fractions. Acetylated histone peptides associated with biotinylated BRD4(1) or BRD4(2) were identified by LC-MS/MS, and the relative peak intensity of individual peptides was expressed as a ratio of peak area of the specific peptide to the sum of all peak areas for acetylated histone peptides in each sample.
See also Figure S7.