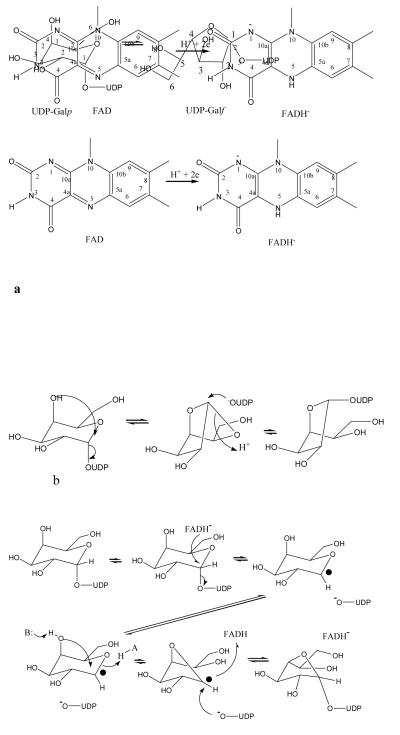
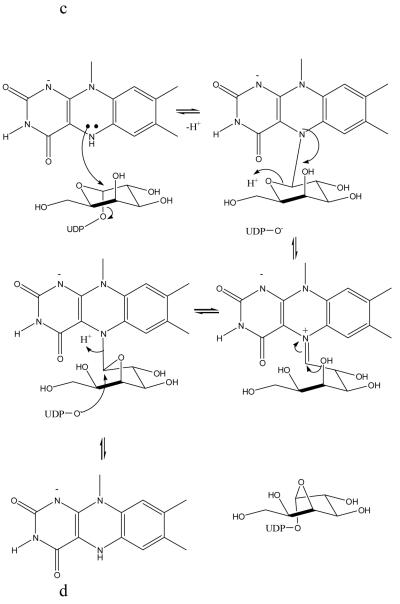
Figure 1.
The mutase enzyme function and structure.
a The chemical reaction catalysed by the mutase enzyme. The cofactor FAD and FADH− are shown. Ring positions numbers are referred to in the text.
b The bicyclic mechanism which does not require direct involvement of the FAD8.
c The redox mechanism in which one electron is transferred to the substrate11. The electron is transferred from FADH- to create a radical which then re-arranges to give product.
d The covalent intermediate mechanism, in the this N5 attacks C1 in a nucleophilic manner. The covalent intermediate then re-arranges to give product. The presence of the covalent intermediate was detected by mass specotrometry12.