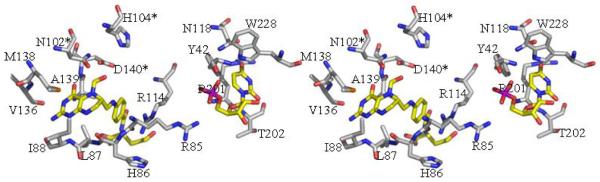
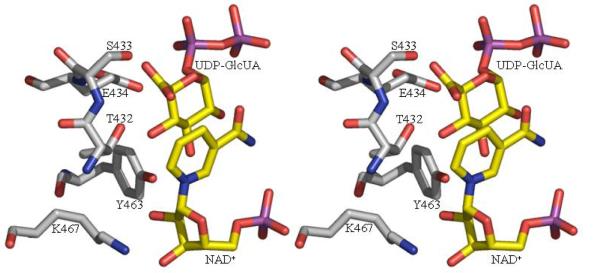
Figure 3.
The active sites of ArnA
3a The active site of formyl transferase. The key catalytic residues are shown (*) as are the two substrate mimics (UMP and N-5-fTHF) located experimentally and those residues which recognize them. The atomic color scheme is the same as Figure 2c
3b The active site of the decarboxylase enzyme. We have modeled in the UDP-GlcUA substrate to generate a conceptual model. The model is based on a superposition of the RmlB substrate complex (42). The catalytic triad residues are shown as are the residues we predict to be important in the decarboxylation step (S433 and E434). These residues superimpose with D135 and E136 of RmlB which are responsible for catalysis of the dehydration step in RmlB transformation (42). The atomic color scheme is the same as Figure 2c.