FIGURE 2. Aminobisphosphonate toxicity for Vγ2Vδ2 T cell can be avoided by pulsing.
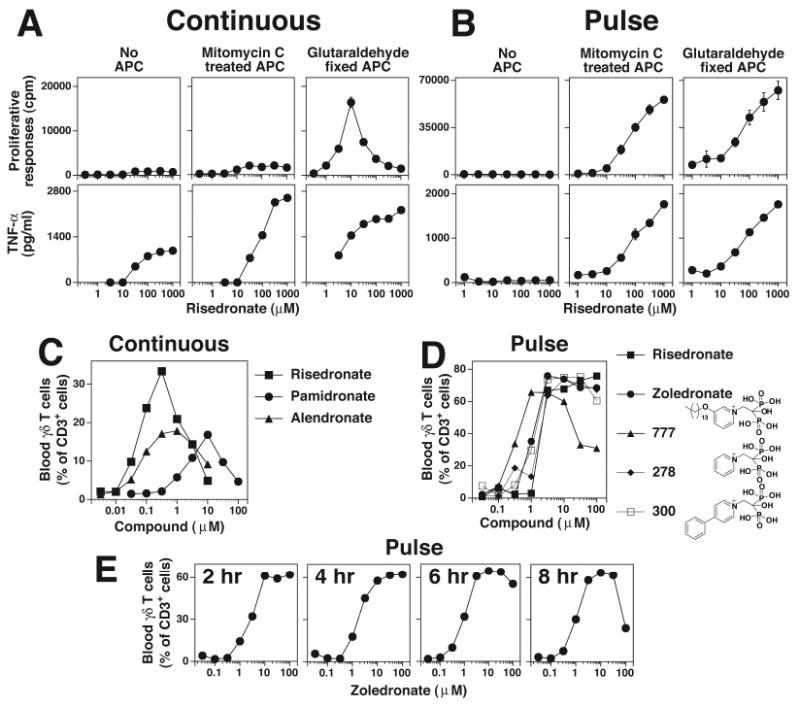
A, Continuous culture of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells with aminobisphosphonates inhibits their proliferation but not TNF-α release. Mit. C treated or glutaraldehyde fixed CP.EBV cells were continuously cultured with risedronate and the CD4+ Vγ2Vδ2 T cell clone, JN.23. Supernatants were collected at 16 h for the measurement of TNF-α. The cells were pulsed with 3H-thymidine and harvested 18 h later. B, APC pulsed with risedronate stimulate both proliferation and TNF-α release. Risedronate was pulsed into APC, washed, and then mixed with the CD4+ Vγ2Vδ2 T cell clone, JN.23. TNF-α and cell proliferation were measured as in A. C, Variable expansion of blood Vγ2Vδ2 T cells with continuous exposure to aminobisphosphonates. PBMC were cultured with various aminobisphosphonates for 10 days and Vγ2Vδ2 T cells and CD3+ T cells determined by flow cytometry. D, Consistent blood Vγ2Vδ2 T cell responses to aminobisphosphonates pulsed into monocytes. PBMC were pulsed for 4 hours with the various aminobisphosphonates. The PBMC were then washed and cultured in the presence of IL-2. After 9 days, Vγ2Vδ2 T cells and CD3+ T cells were determined by flow cytometry. E, Expansion of blood Vγ2Vδ2 T cells in PBMC pulsed with zoledronate. PBMC were pulsed for the indicated time with zoledronate, washed, and cultured in the presence of IL-2. After 9 days, Vγ2Vδ2 T cells and CD3+ T cells were determined by flow cytometry.
