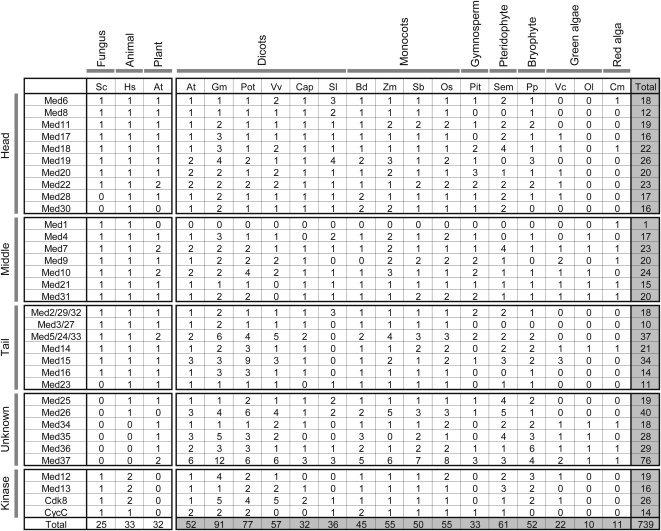
Figure 2.
The distribution of putative Med proteins across the plant kingdom. The Med subunits are grouped as head, middle, tail, and kinase module according to Bourbon (2008). The unknown group has members whose positions in the complex are unassigned. The left panel lists the number of biochemically purified Med proteins in S. cerevisiae (Sc), human (Hs), and Arabidopsis (At). The right panel reports the number of homologs predicted in the study for diverse plants belonging to various groups (marked at the top of each respective group) of the plant kingdom. The total numbers of Med proteins identified for an organism and for an individual Med subunit are represented in shaded boxes at the ends of the columns and rows, respectively. Organisms are as follows: G. max (Gm), P. trichocarpa (Pot), V. vinifera (Vv), C. papaya (Cap), S. lycopersicum (Sl), B. distachyon (Bd), Z. mays (Zm), S. bicolor (Sb), O. sativa (Os), P. taeda (Pit), S. moellendorffii (Sem), P. patens (Pp), V. carteri (Vc), O. lucimarinus (Ol), and C. merolae (Cm).