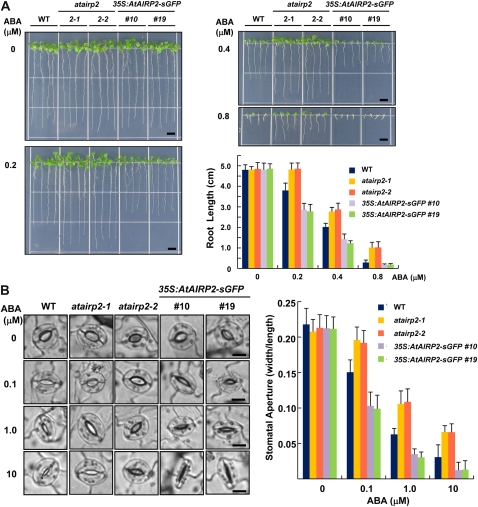
Figure 5.
Root growth and stomatal aperture of wild-type, atairp2, and 35S:AtAIRP2-sGFP plants in response to ABA treatment. A, Root-growth phenotypes of the wild type (WT), two atairp2 mutant alleles (atairp2-1 and atairp2-2), and AtAIRP2 overexpressors (transgenic lines 10 and 19) in response to different concentrations (0, 0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 μm) of ABA. Sterilized seeds were imbibed in water for 2 d and grown vertically on MS medium supplemented with the indicated concentrations of ABA for 10 d. Root growth patterns were monitored and analyzed using Scion Image software. Data represent means ± sd (n = 20). Bars = 0.5 cm. B, Stomatal aperture of the wild type, two atairp2 mutant alleles (atairp2-1 and atairp2-2), and AtAIRP2 overexpressors (transgenic lines 10 and 19) in response to different concentrations (0, 0.1, 1.0, and 10 μm) of ABA. Mature leaves from wild-type, atairp2 allele, and AtAIRP2-overexpressing plants were treated with a stomatal opening solution for 2 h and incubated with the indicated concentrations of ABA for 2 h. Stomata on abaxial surfaces were photographed by light microscopy. Bars = 10 μm. Stomatal aperture (the ratio of width to length) was quantified using at least 30 guard cells from each sample. Data represent means ± sd (n = 30). [See online article for color version of this figure.]