Figure 1.
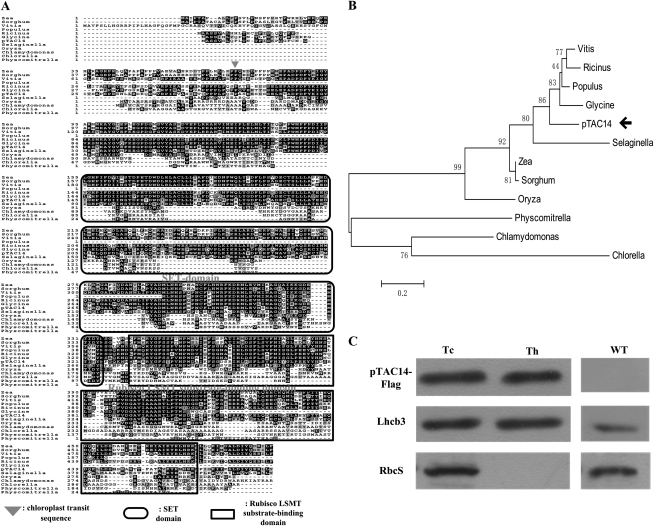
Sequence alignment, phylogenetic analysis, and subcellular location of the pTAC14 protein. A, Alignment analysis between pTAC14 and its homologs from R. communis, O. sativa, Z. mays, V. vinifera, S. bicolor, G. max, S. moellendorffii, P. trichocarpa, C. variabilis, C. reinhardtii, and P. patens. The arrowhead denotes the putative cleavage site of the transit peptide in the pTAC14 protein. The rounded rectangular box denotes the SET domain, and the square rectangular box denotes Rubisco LMST substrate-binding domains of the pTAC14 protein. B, Phylogenetic analysis of the pTAC14 protein and its homologs supports a close relationship among R. communis, O. sativa, Z. mays, V. vinifera, S. bicolor, G. max, S. moellendorffii, P. trichocarpa, C. variabilis, C. reinhardtii, and P. patens. C, pTAC14 is located in the chloroplast and is associated with the thylakoid. The fractionation of transgenic Arabidopsis seedling chloroplasts was performed with anti-FLAG, anti-Lhcb3, and anti-RbcS antibodies. Wild-type chloroplasts (WT) were used as controls. Tc, Total chloroplast protein; Th, thylakoid fraction.