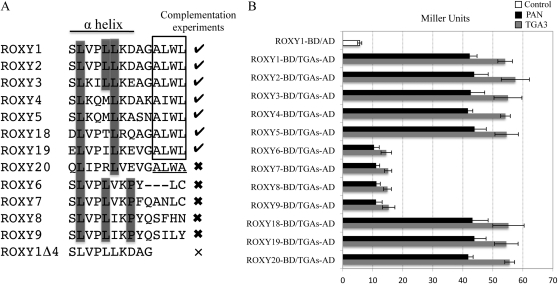
Figure 5.
Comparison of L**LL motifs for different ROXYs and analyses of their competence to interact with TGA proteins. A, Alignment of C-terminal sequences comprising the L**LL motif of the ROXY1 α5 helix for representative ROXYs. Check marks indicate ROXYs capable of complementing the roxy1 mutant, thick crosses denote previously tested ROXYs that failed to complement the ROXY1 mutant, and the thin cross represents a mutagenized ROXY1 lacking the C-terminal four amino acids. The C-terminal four amino acids A(L/I)WL conserved for all the ROXYs complementing the roxy1 mutant are boxed, and the C-terminal four amino acids ALWA of the noncomplementing ROXY20 are underlined. Leu residues (corresponding to L1–L3 in ROXY1) are indicated for all the tested ROXYs, and conserved Pro residues for four of the five noncomplementing ROXYs are highlighted by a gray box. Amino acid sequences corresponding to the ROXY1 α5 helix are shown below a solid line. B, Quantitative yeast protein interaction data of representative ROXYs tested in complementation experiments. Data are means ± sd of three independent experiments.