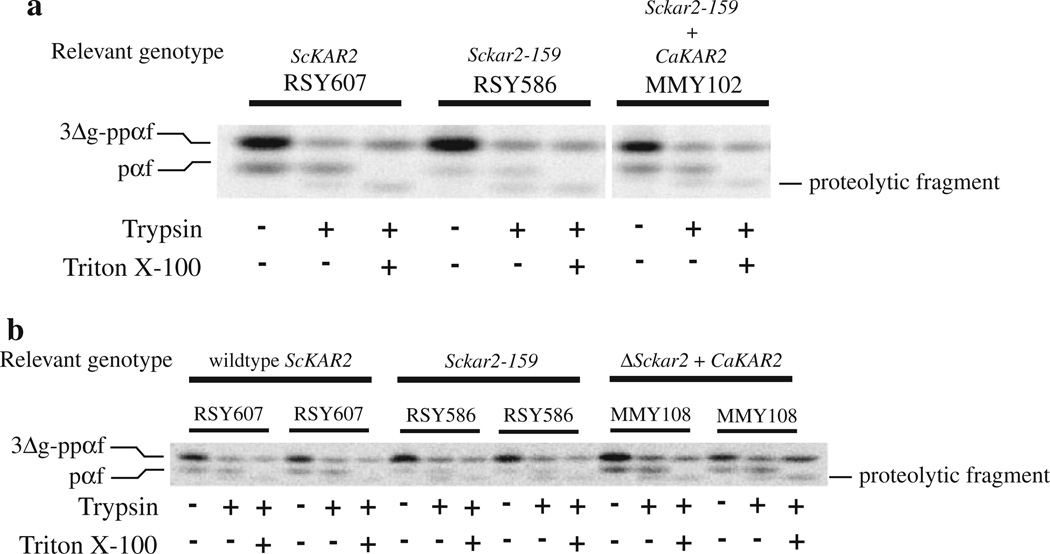
Fig. 5.
The C. albicans Kar2 protein can replace the function of S. cerevisiae Kar2p during translocation in vitro. ER microsomes were prepared from a wild-type S. cerevisiae strain (RSY607), a kar2 mutant strain (RSY586) and strain MMY102 (a), which is RSY586 expressing wild-type C. albicans Kar2p, or MMY108 (b), which is a S. cerevisiae strain containing C. albicans Kar2p as the only form of Kar2p in the cells. These microsomes were used in in vitro translocation reactions using 35S-labeled 3Δg–ppαf as the translocation substrate (see text). After translocation, the reactions were split equally into three tubes and either left untreated, or treated with trypsin or trypsin and Triton X-100. The proteins were then TCA precipitated and resolved by 18% SDS-PAGE in gels containing urea and subjected to phosphorimage analysis. The presence of trypsin-protected pαf indicates substrate translocation. Duplicate translocation reactions are shown in b