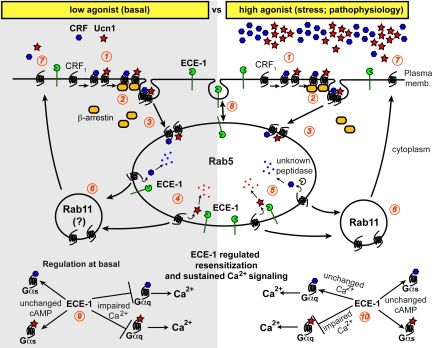
Fig. 9.
ECE-1 activity determines differential recycling fate of CRF1 upon Ucn1- or CRF-stimulation depending on agonist dose. 1, CRF or Ucn1 binds and activates CRF1. 2, βARR transiently associate with the receptor to mediate desensitization. 3, CRF1 is endocytosed to Rab5 containing early endosomes. 4, Under low agonist conditions, ECE-1 facilitates dissociation of the ligands from CRF1, allowing CRF1 to recycle and resensitize. 5, Under high agonist conditions, ECE-1 facilitates removal of Ucn1 from CRF1, thereby causing Ucn1-mediated receptor to recycle and resensitize. CRF then dissociates from CRF1 by an ECE-1 independent mechanism (presumably by an unknown peptidase?) that allows the freed receptor to recycle and resensitize. 6, Rab11 knockdown studies suggest that CRF1 recycles and resensitizes via a Rab11-dependent pathway. The question mark (?) indicates that we did not test this at a low agonist concentration. 7, Recycled CRF1 is available for resensitization by CRF or Ucn1. 8, ECE-1 is also present at the plasma membrane and gets constitutively shuttled between the plasma membrane and endosomes. 9, At low/basal agonist concentrations, ECE-1 activity regulates both Ucn1- and CRF-mediated Ca2+ signaling, whereas ECE-1 does not appear to affect Gαs-coupled CRF1 and downstream cAMP signaling. 10, At high/pathophysiological agonist concentrations, ECE-1 activity regulates Ucn1-, but not CRF-mediated Ca2+ signaling, whereas ECE-1 does not appear to affect CRF1-mediated cAMP signaling. memb., Membrane.