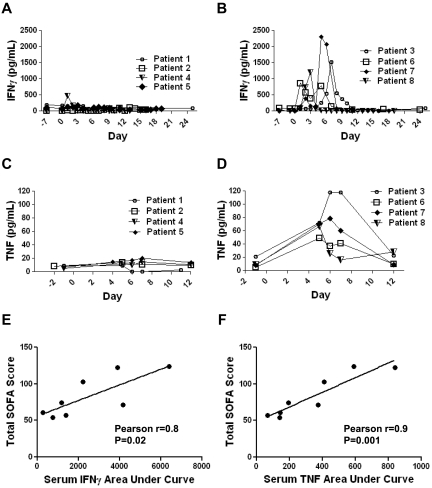
Figure 6.
Elevations in serum levels of IFNγ and TNF occurred in some patients after infusions of anti–CD19-CAR–transduced T cells. (A) Patients 1, 2, 4, and 5 did not have prominent elevations of serum IFNγ after cell infusion. (B) Patients 3, 6, 7, and 8 had prominent elevations of serum IFNγ after cell infusion. (C) Patients 1,2,4, and 5 did not have prominent elevations of serum TNF after cell infusion. (D) Patients 3, 6, 7, and 8 had prominent elevations of serum TNF after cell infusion. For panels A through D, day 0 is the day of CAR-transduced T-cell infusion, and serum IFNγ and TNF were determined by standard ELISAs performed on serum samples. (E) The correlation between the total sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) scores of each patient and the areas under the curves of each patient's serum IFNγ level (pg/mL)×(days) from the day of CAR-transduced T-cell infusion until day 11 after T-cell infusion is shown. The total SOFA scores and the areas under the curves of serum IFNγ were correlated (Pearson r = 0.8, P = .02). (F) The correlation between the total SOFA scores of each patient and the areas under the curves of each patient's serum TNF level (pg/mL)×(days) from the day before CAR-transduced T-cell infusion until day 12 after T-cell infusion is shown. The total SOFA scores and the areas under the curves of serum TNF were correlated (Pearson r = 0.9, P = .001).