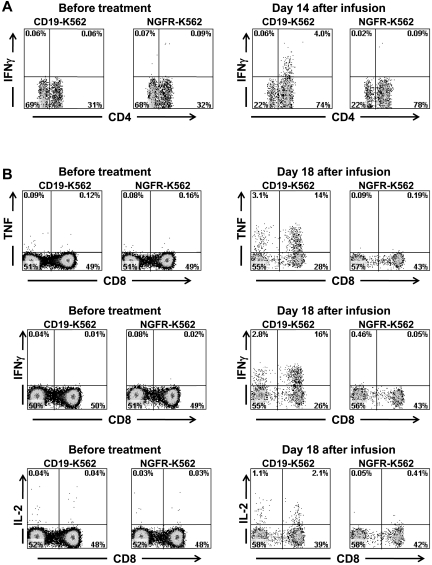
Figure 7.
Large numbers of T cells producing cytokines in a CD19-specific manner can be detected in the blood of patients after anti–CD19-CAR–transduced T-cell infusions. (A) PBMCs were collected from patient 3, 14 days after infusion of CAR-transduced T cells. When the PBMCs were cultured for 6 hours with CD19-K562 cells that expressed CD19, a population of CD4+ cells that produced IFNγ was detected; in contrast, when the PBMCs were cultured with the control cells NGFR-K562 that lack CD19 expression, T cells did not produce IFNγ. PBMCs collected before the anti–CD19-CAR–transduced T-cell infusion did not produce IFNγ after incubation with either CD19-K562 or NGFR-K562. Plots are all gated on CD3+ lymphocytes. (B) PBMCs were collected from patient 7, 18 days after infusion of CAR-transduced T cells. When the PBMCs were cultured for 6 hours with CD19-K562 cells that expressed CD19, T cells that produced IFNγ, TNF, and IL-2 were detected. When the PBMCs were cultured with the control cells NGFR-K562 that lack CD19 expression, T cells did not produce IFNγ, TNF, or IL-2. PBMCs collected before the anti–CD19-CAR–transduced T-cell infusion did not produce IFNγ, TNF, or IL-2 after incubation with either CD19-K562 or NGFR-K562. Plots are all gated on CD3+ lymphocytes.