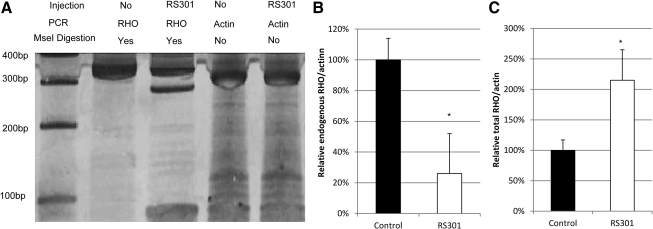
FIG. 2.
Subretinal injection of AAV-RS301 leads to an increase in total rhodopsin RNA. (A) Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR products of mouse and human rhodopsin mRNAs were prepared with a common set of primers in the same reaction (Mao et al., 2011). Subsequent incubation with restriction enzyme MseI digested RHO301 into bands of 283 and 70 bp, and undigested human P23H RHO and mouse Rho had the same 353-bp band. RT-PCR products from uninjected eyes contained only the uncut 353-bp product after MseI treatment. Amplification products of β-actin mRNA from the same retinas (without MseI digestion) were used for normalization. (B) Endogenous rhodopsin mRNA levels (human P23H RHO and mouse Rho) were reduced in RS301-treated eyes (open column) (p<0.05; n=3). (C) Total rhodopsin mRNA (human P23H RHO, mouse Rho, and RHO301) increased in RS301-injected eyes (open column) (p<0.05; n=3). In (B) and (C) the ratio of rhodopsin to actin PCR products in untreated eyes was set to 100%.