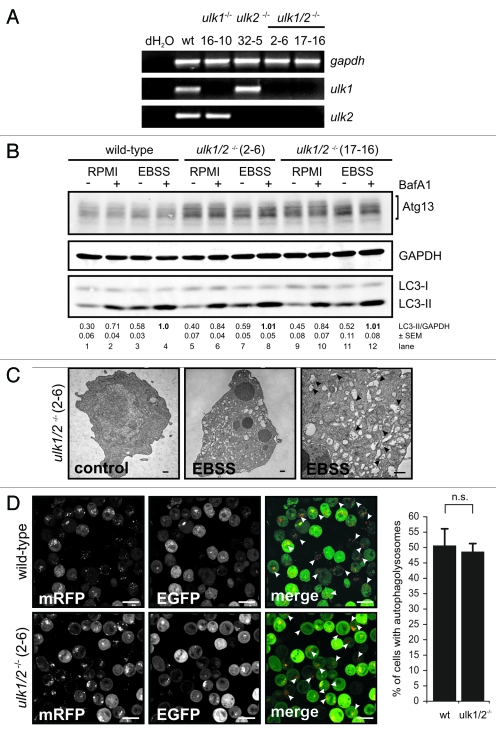
Figure 3.
Ulk1 and Ulk2 are dispensable for autophagy induction in DT40 cells. (A) DT40 cells deficient for Ulk1 (ulk1−/−), Ulk2 (ulk2−/−) or Ulk1 and Ulk2 (ulk1/2−/−) were generated by gene targeting and loss of wild-type alleles was confirmed by genomic PCR (for details see Figure S2). The absence of ulk1 and ulk2 transcripts was verified by RT-PCR. (B) Wild-type cells and two independent double deficient ulk1/2−/− clones (2–6 and 17–16) were incubated in full medium (RPMI) or EBSS in the presence or absence of 10 nM BafA1 for 1 h. Equal amounts of protein from cleared cellular lysates were analyzed for Atg13, GAPDH and LC3 by immunoblotting. LC3-II/GAPDH ratios are represented as mean values of three independent experiments ± SEM (C) ulk1/2−/− cells (clone 2–6) were incubated in normal growth medium (control) or EBSS for 2 h, cells were fixed and analyzed by transmission electron microscopy. For starvation condition, a representative cell is shown in two different magnifications. Autophagosomes are indicated by black arrow heads in the image with higher magnification (bars: 500 nm). (D) ulk1/2−/− cells (clone 2–6) retrovirally transfected with cDNA encoding mRFP-EGFP-rLC3 were incubated in EBSS for 2 h and analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The mRFP signal is shown in red and the EGFP signal in green in the merged image. Autolysosomes are indicated by white arrow heads (bars: 10 µm). The percentage of cells with autolysosomes (> 100 cells/experiment) is represented as mean value ± SD from three independent experiments. n.s. indicates a non-significant difference between wild-type and ulk1/2−/− cells (Student’s t-test).