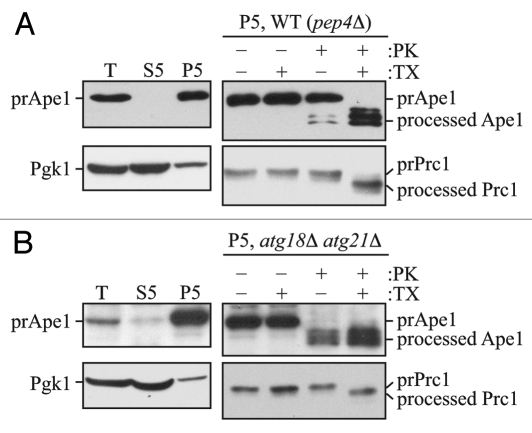
Figure 1.
The prApe1 protease protection assay. (A) Wild-type (atg18Δ atg21Δ pep4Δ) cells expressing Atg18-PA and Atg21 (WT) or (B) atg18Δ atg21Δ pep4Δ cells were grown to exponential phase in YPD medium and converted to spheroplasts.16 The spheroplasts were starved for 1 h in SD-N medium supplemented with 1.2 M sorbitol to induce autophagy, collected by centrifugation, resuspended in osmotically balanced lysis buffer, and then disrupted. In order to remove unbroken cells, the lysate was subjected to centrifugation at 300 × g. The resulting total lysate (T) was further separated into 5,000 × g lysate (S5) and pellet (P5) fractions. The P5 fraction from each strain was split into four parts and subjected to different treatments: No treatment, treatment with 0.4% Triton X-100 (TX), treatment with proteinase K (PK), or treatment with proteinase K in the presence of 0.4% Triton X-100. The samples were precipitated using 10% TCA, acetone washed and analyzed by immunoblot using anti-Ape1 antiserum. Lysis conditions were verified by immunoblot analysis using the anti-Pgk1 and anti-Ape1 antisera. To verify the integrity of organellar membranes in the P5 fractions, maturation of the precursor form of Prc1 was examined. This figure includes data previously published in reference 16, which are reproduced by permission of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and Elsevier, copyright 2010.