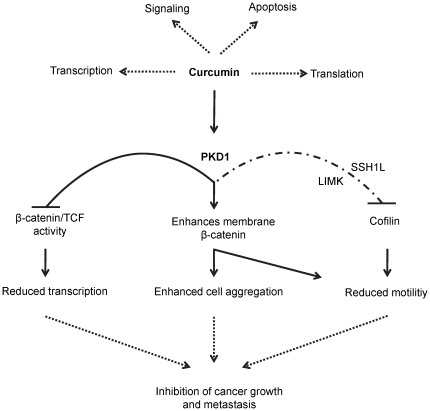
Figure 9. Schematic diagram showing possible signaling mechanisms modulated by curcumin mediated PKD1 activation.
Curcumin modulates a number of molecular pathways within the cancer cells including PKD1 signaling. Curcumin may suppress prostate cancer growth and metastasis by activating PKD1, which in turn may inhibit cell growth through the inhibition of β-catenin/TCF transcription activity, enhance cell-cell aggregation via enhanced translocation of β-catenin to the cell membrane and inhibit cell motility either directly by enhancing cell-cell aggregation and/or phosphorylating and inhibiting the function of sling shot 1 like (SSH1L) phosphatase or indirectly (dashed lines) by negatively regulating the expression of active cofilin via indirectly activating LIM kinase (LIMK).