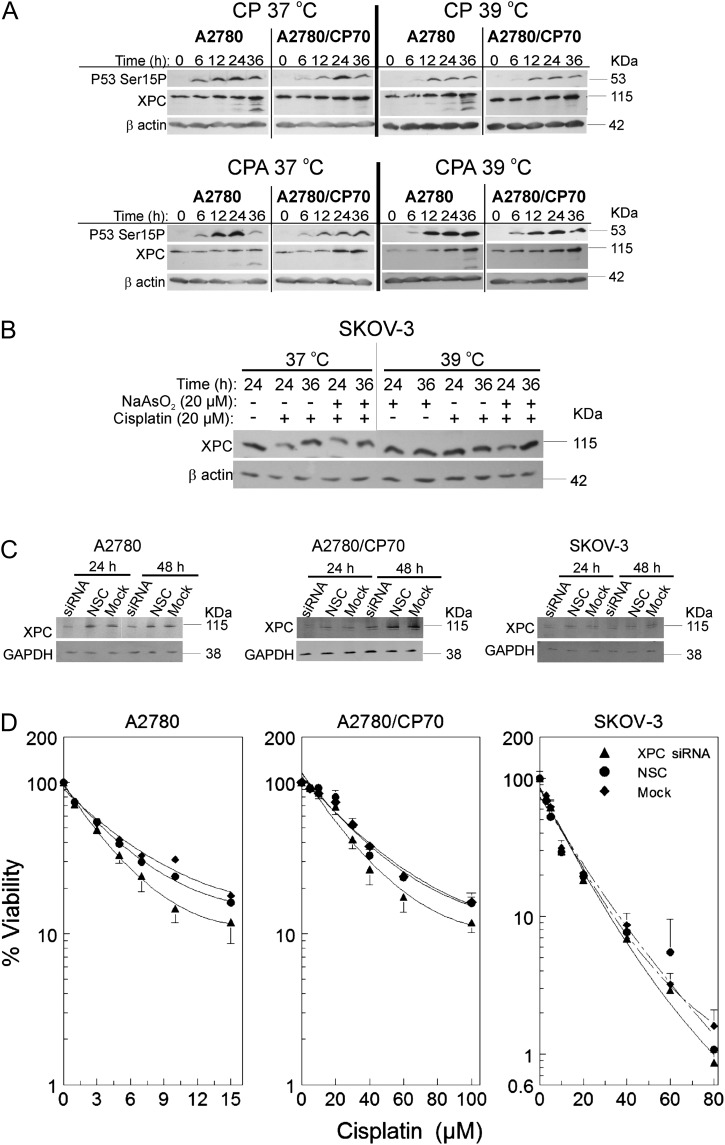
FIG. 4.
Suppression of cisplatin-induced XPC by sodium arsenite and hyperthermia and the effect of XPC siRNA transfection on cisplatin cytotoxicity. (A and B) Western blot analyses of XPC and p53Ser15P in A2780 and A2780/CP70 cells. Cells were treated with their IC50 cisplatin (CP; A2780, 4μM; A2780/CP70, 40μM; SKOV-3, 20μM) or CP plus 20μM sodium arsenite (CPA) at 37 or 39°C for 1 h. After treatment, cells were washed with PBS and incubated in drug-free media. Protein lysates were prepared at 0, 6, 12, 24, and 36 h for Western blot analyses. ß-actin is the loading control. Data are representative blots of three independent experiments. (B) Western blot analyses of XPC in SKOV-3 cells. Cells were treated with cisplatin ± sodium arsenite as indicated for 1 h, then washed and reincubated in drug-free media for 24 or 36 h. Then, lysates were prepared for Western blot analyses. (C) Western blot analyses of XPC after XPC siRNA transfection. (D) Viability of A2780, A2780/CP70, and SKOV-3 cells after XPC siRNA (▴), NSC (•), or mock (♦) transfection. Cells were transfected with XPC smart pool siRNA, NSC, or mock. At 23 h after transfection, cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of cisplatin (D) or respective IC50 cisplatin (CP; A2780, 4μM; A2780/CP70, 40μM; SKOV-3, 20μM) (C). After treatment, cells were washed twice with PBS and incubated in drug-free media. MTT assay was performed 5 days after treatment. Protein lysates for Western blot analyses were prepared at 24 and 48 h after transfection. Data in panels A, B, and C are representative blots for three independent experiments. Data in panel D are plotted as means ± SD of three independent experiments.