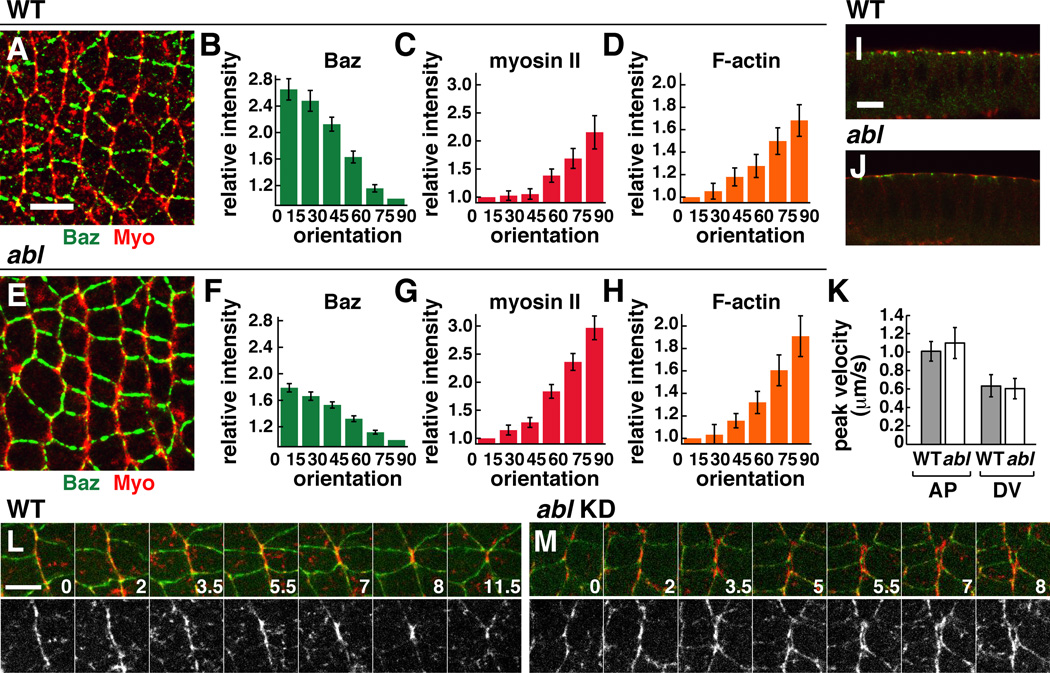
Figure 4. Abl is not required for planar polarized actomyosin localization and contractility.
(A–J) Localization of myosin II (red) and Baz/Par-3 (green) in WT (A,I) and abl mutant (E,J) embryos at stage 7. Quantitation of planar polarity in WT (B–D) and abl (F–H). Values were normalized to the mean intensity of edges oriented at 0–15° (for myosin II and F-actin) or at 75–90° (for Baz), where 0° is parallel to the AP axis. n=7–12 embryos, 77–247 edges/embryo. Planar polarity is significantly decreased in abl mutants for Baz (p=0.00017), and is only slightly increased for myosin (p=0.036) and F-actin (p=0.33). (K) Peak retraction velocities after ablation in WT (n=10 AP, 6 DV ablations) and abl (n=6 AP, 7 DV ablations). (L,M) Stills from time-lapse movies in WT and abl knockdown (KD) embryos. E-cadherin:GFP (green), Myo:mCherry (red). Time in min. Anterior left, dorsal up. Cross sections shown in I,J. Bars, 10 µm in A–J, 5 µm in L,M. See also Figure S2 and Movies S3,S4.