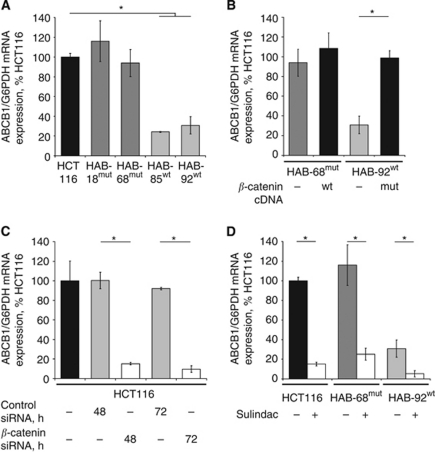
Figure 1.
Gain-of-function β-catenin regulates ABCB1 mRNA expression in a dominant fashion. (A) ABCB1 mRNA expression analysis in HCT116, HAB-18mut, HAB-68mut, HAB-85wt and HAB-92wt cells. High ABCB1 levels were observed in the cell line HCT116 and its derivatives harbouring mut β-catenin, low ABCB1 expression in the derivatives with wt β-catenin. ABCB1 mRNA expression was determined by quantitative real-time RT–PCR; values represent the ratios of ABCB1 and G6PDH control mRNA (HCT116 cells: set 100%). Experiments were performed in duplicate and average values are shown. (B) ABCB1 mRNA expression in knockout derivatives with reconstituted β-catenin genotype. Transfection of HAB-68mut cells with wt β-catenin cDNA did not change ABCB1 expression levels. Transfection of HAB-92wt cells with mut β-catenin cDNA, however, induced ABCB1 expression up to four-fold. (C) ABCB1 mRNA expression in HCT116 cells following treatment with β-catenin siRNA. Knockdown of ABCB1 expression by β-catenin siRNA is shown. Transfection of control siRNA had no effect. (D) Treatment of HCT116, HAB-68mut and HAB-92wt cells with sulindac (100 μM; 24 h). ABCB1 expression levels in solvent-treated cells were dependent on β-catenin genotype. Sulindac treatment reduced ABCB1 mRNA expression in HCT116, HAB-68mut and HAB-92wt cells. *P<0.05.