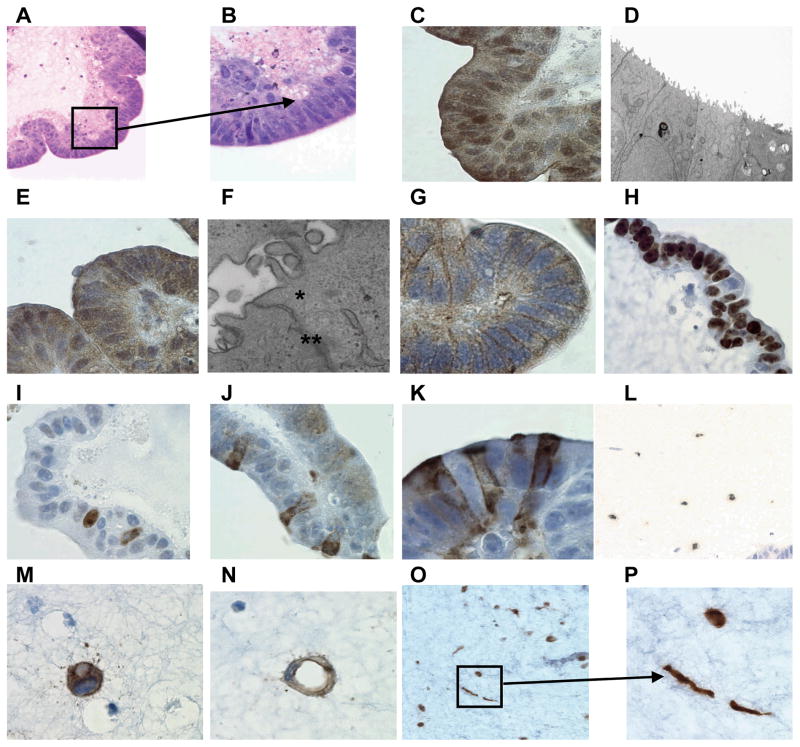
Figure 1.
Epithelial cell differentiation. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of 14 day-cells cultured in the 3-D microgravity model: tissues were stained purple and scaffold stained pink. Lower (A) and higher magnification (B) shows the presence of polarized epithelial cells with microvilli seen collectively as a fuzzy fringe in the apical surface of the epithelium. The presence of microvilli was further confirmed by immunochemical staining using the anti-villin mouse mAb (C) and by electron microscopy (D). Presence of tight junctions was detected by Immunochemical staining by using an anti-ZO-1 polyclonal rabbit antiserum (E) or electron microscopy (F) (tight junctions (*) and desmosome (**)). Immunochemical staining was also used to detect E-cadherin using the anti-E-cadherin mouse mAb (G). The presence of proliferating cells was detected at day 5 (H) and day 15 (I) by using the anti-Ki67 rabbit mAb. The presence of multi-lineage differentiation was also observed: goblet cells using the anti-MUC-2 monoclonal antibody (J) and M cells using the anti-Sialyl Lewis Antigen mAb at day 15 (K). Cells from a 17-day 3-D organotypic culture were also stained by immunochemistry for lymphocytes using the anti-CD45 mAb (L) (low magnification), for endothelial cells using the anti-CD31 mAb (M) (sprouting) (N) (vessel-like conduit formation)(high magnification), and for fibroblasts using the anti-vimentin mAb at low (O) and (P)(spindle shaped rounded-fat cell-like shaped) at high magnification.