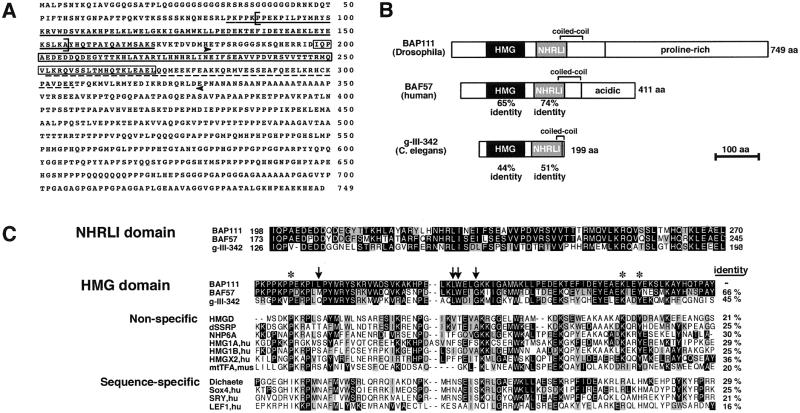
Figure 1.
Sequence and predicted domains of the BAP111 protein. (A) Amino acid sequence of the BAP111 protein. The HMG domain is indicated by a single underline, the NHRLI domain is boxed, and the coiled-coil region is indicated by a dashed line. Arrowheads mark the portion of BAP111 used to generate polyclonal antibodies. Brackets enclose the amino acids deleted in BAP111ΔHMG. (B) Domains of the BAP111 protein. Domains are drawn to scale. Percent amino acid identity to BAP111 is indicated below domains. The proline-rich region of BAP111 (amino acids 360–749) is 30.5% proline. BAF57 is a subunit of BRG1/hBRM complexes (27). g-III-342 is the translation of a Caenorhabditis elegans gene predicted by Genie (48–50) and annotated in Intronerator (43). This sequence is largely confirmed by the 5′ EST yk538e12.5. There is no 3′ EST currently available to confirm the C terminus. (C) Sequence alignment of conserved domains of BAP111. In the NHRLI domain alignment, black indicates identity and gray indicates conservation in two or more residues at a given position. Alignment of the HMG domains is similarly coded but homology is to BAP111. Percent identity to BAP111 is indicated at the right of each HMG-domain sequence. Residues cited in the text as marking distinctions between sequence-specific and nonspecific HMG domains are marked above the alignment. Asterisks specify residues conserved in nonspecific HMG domains; arrows specify residues conserved in sequence-specific HMG domains.