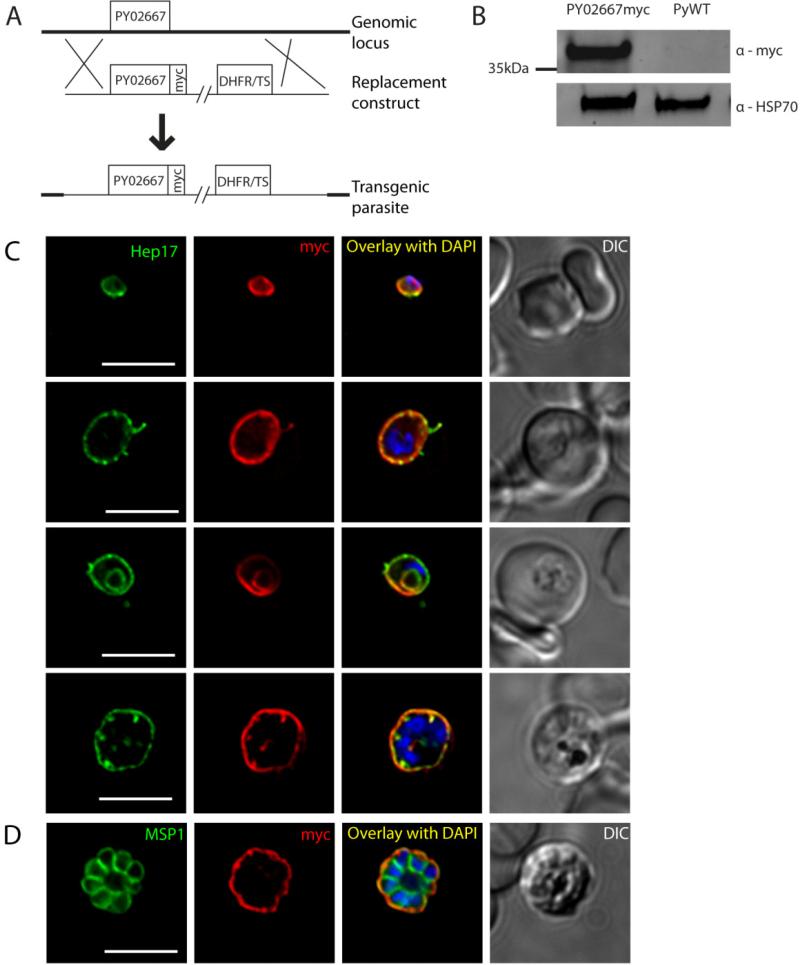
Figure 2.
Protein expression and localization of PY02667myc in blood stages. (A) Schematic representation of the strategy used to replace PY02667 in P. yoelii with a construct encoding a c-terminal fusion of the 4x myc epitope to PY02667. (B) Western blot of lysates from mouse blood infected with asynchronous PY02667myc parasites or WT control. (C) Immunofluorescence (IFA) microscopy images of PY02667myc blood stages labeled with anti-myc or anti-Hep17 antibodies, and DAPI (to label DNA). A differential interference contrast (DIC) image of the liver section is shown to the right. Overlap of myc signal with Hep17 indicates localization of PY02667myc to the PVM. PY02667myc is expressed in all stages of intraerythrocytic development. Stages are distinguishable on the basis of morphology and DAPI staining; small uninucleate ring stages (top) grow into uninucleate trophozoites (middle rows). Myc staining persists throughout karyokinesis with the onset of schizogony (bottom). Infected erythrocytes are shown with differential interference contrast (DIC). Scale bars = 5 micrometers. (D) IFA of blood stage PY02667myc schizont, labeled with anti-myc or anti-MSP1 antibodies, and DAPI. Myc signal remains in the PVM surrounding the newly formed daughter merozoites, indicated with the PPM marker MSP1. Scale bar = 5 micrometers.