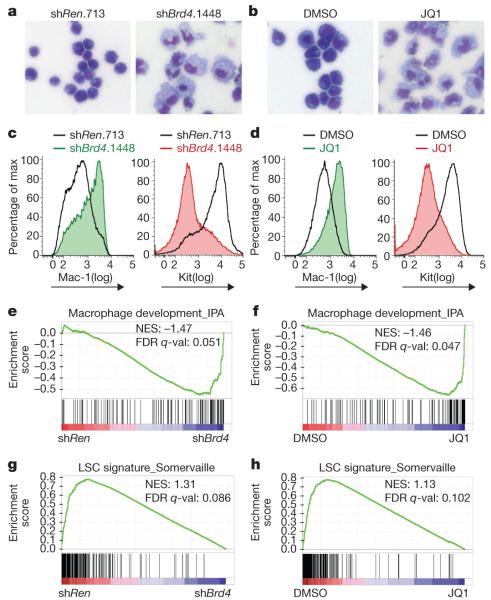
Figure 3. Brd4 inhibition leads to myeloid differentiation and leukaemia stem-cell depletion.
a, b, Light microscopy of May–Grünwald/Giemsa-stained MLL-AF9/NrasG12D leukaemia cells after 2 days of doxycycline-induced shRNA expression or 2 days of JQ1 treatment (100 nM). Expression of shRNA was induced in TRMPV-transduced leukaemia cells. Imaging was performed with a ×40 objective. Representative images of three biological replicates are shown. c, d, FACS analysis of Mac-1 and Kit surface expression after 4 days of shRNA expression or 2 days of JQ1 treatment (100 nM). A representative experiment of three biological replicates is shown. e–h, GSEA plots evaluating changes in macrophage and LSC gene signatures upon Brd4 inhibition. In e and g, RNA for expression arrays was obtained from sorted dsRed+/shRNA+ cells (shRen versus three different Brd4 shRNAs) after 2 days of doxycycline induction. In f and h, microarray data were obtained from leukaemia cells treated for 2 days with DMSO or 100 nM JQ1. NES, normalized enrichment score; FDR q-val, false discovery rate q-value (the probability that a gene set with a given NES represents a false-positive finding).