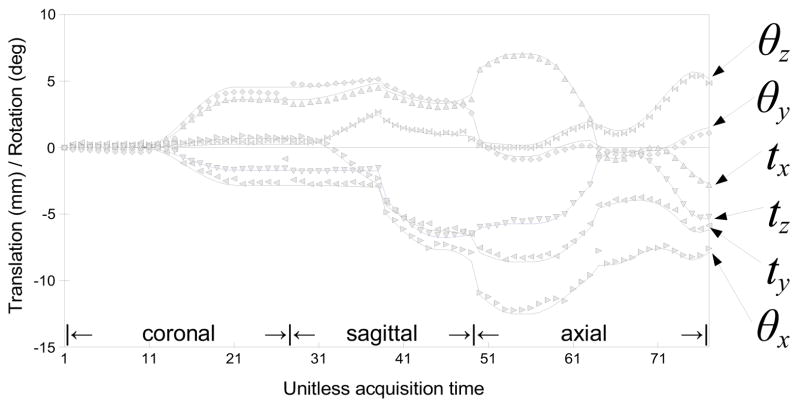
Fig. 9.
Fetal motion was simulated by adding two motion points during the simulated acquisition of each stack, where the amount of motion is randomly chosen within a preset range. The motion was then temporally smoothed using a Gaussian kernel for physical reality (solid lines). The symbols indicate the estimated motion parameters obtained by registering slices using the proposed method.