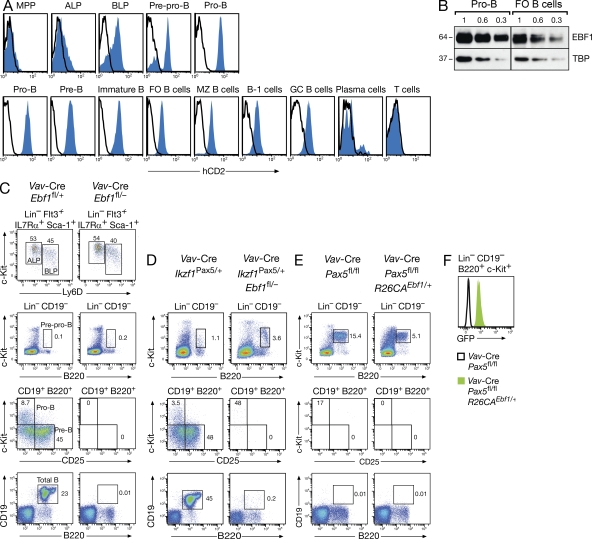
Figure 1.
Nonredundant functions of EBF1 and Pax5 in early B cell development. (A) Ebf1ihCd2/+ (blue) and WT (black line) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry for human (h) CD2 expression in different progenitors, B cell types, and T cells, which were defined as described in Materials and methods. (B) Expression of EBF1 protein in cultured pro–B cells and MACS-sorted FO B cells from lymph nodes. One of two immunoblot experiments is shown. Numbers indicate the relative proportion of nuclear extracts analyzed. The EBF1 protein abundance is normalized to expression of the TBP, and the size (kilodaltons) of the two proteins is indicated to the left. (C and D) B cell development in Vav-Cre Ebf1fl/− mice with or without ectopic Pax5 expression from the Ikzf1Pax5 allele. Progenitor and B cell types were investigated by flow cytometry of bone marrow cells isolated from mice of the indicated genotypes. The relative percentage of each cell type is indicated in the respective quadrant, and the gating is shown above the FACS plot. The different cell types were defined as described in Materials and methods. (E and F) B cell development in Vav-Cre Pax5fl/fl mice with or without ectopic EBF1 expression from the R26CAEbf1 allele (E). GFP expression, indicating EBF1 expression, in Pax5-deficient progenitors of Vav-Cre R26CAEbf1/+ Pax5fl/fl mice (F). Number of mice of each genotype analyzed: n = 8 (C); n = 5 (D); and n = 3 (E).