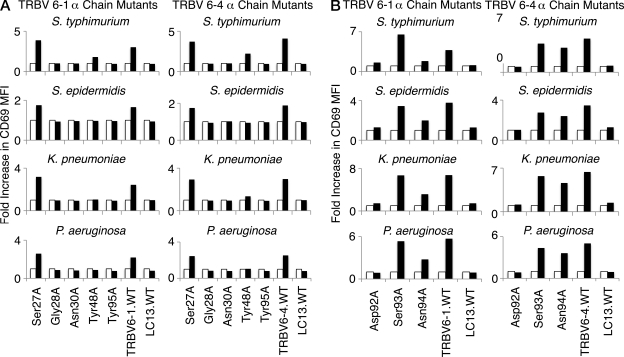
Figure 6.
The α chain residues crucial to MAIT TCR recognition are conserved in two other MAIT TCRs. The mutant α chain residues observed to diminish bacterial activation in SKW3.TRBV20 cell lines (Gly28Ala, Asn30Ala, Tyr48Ala, Asp92Ala, Asn94Ala, and Tyr95Ala, as well as control Ser27Ala and Ser93Ala mutations) were introduced into the MAIT.TRBV6-1 and MAIT.TRBV6-4 TCRs before transduction of MAIT TCR genes into SKW3 cells. SKW3.TRBV6-1 and SKW3.TRBV6-4 cell lines transduced with mutants Ser27Ala, Gly28Ala, Asn30Ala, Tyr48Ala, or Tyr95Ala (A), or mutants Asp92Ala, Ser93Ala, or Asn94Ala (B) were then tested for activation by S. typhimurium, S. epidermidis, K. pneumoniae, and P. aeruginosa. Shaded bars show the fold increase in CD69 surface expression (fold increase in MFI) of mutant SKW3.TRBV6-1 or mutant SKW3.TRBV6-4 cells co-incubated with C1R cells infected with bacteria at an MOI of 100 compared with SKW3.TRBV6-1 or SKW3.TRBV6-4 cells co-incubated with uninfected C1R cells (open bars). These experiments were performed three times, with similar results.