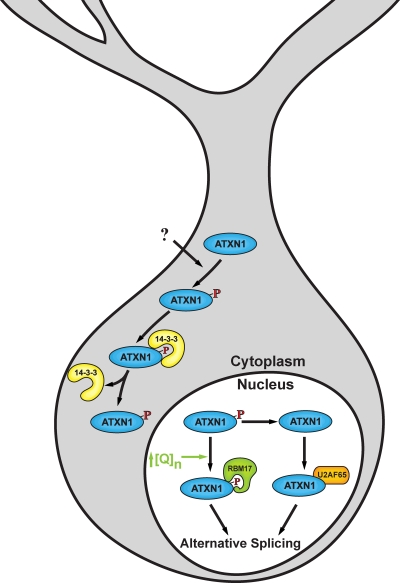
Figure 1.
An ATXN1 cellular pathway. ATXN1 is phosphorylated at S776 in the cytoplasm upon which it forms a complex with 14-3-3. Association with 14-3-3 blocks dephosphorylation of pS776 and transport of ATXN1 to the nucleus. Thus, nuclear transport of ATXN1 requires dissociation from 14-3-3, the regulation of which has yet to be determined. In the nucleus, ATXN1 is involved in alternative splicing by virtue of its interaction with RBM17 when phosphorylated on S776, or with U2AF65 after dephosphorylation of pS776. ↑[Q]n indicates that an increased interaction of expanded polyQ ATXN1 with RBM17 is hypothesized to be critical for driving disease in cerebellar Purkinje cells.