Figure 2.
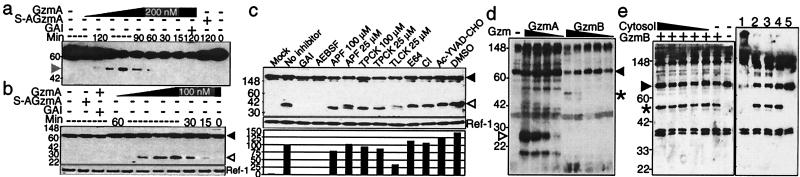
GzmA and GzmB cleave laminB in isolated nuclei independently of caspase activation. (a and b) Four-fold dilutions of GzmA ranging from 0.4 to 200 nM were added to isolated HeLa nuclei for the indicated times. Full-length laminB is indicated by a black arrowhead, the C-terminal 25-kDa laminB fragment by a white arrowhead, and the N-terminal 46-kDa fragment by a gray arrowhead. LaminB degradation requires the active Ser protease because S-AGzmA does not induce cleavage, and the reaction is blocked by GAI. (c) Ser protease inhibitors, but not caspase or other protease inhibitors, reduce lamin cleavage in HeLa nuclei by GzmA. HeLa nuclei were incubated for 1 h with nothing (mock) or with 100 nM GzmA in the presence of no inhibitor, DMSO, or the indicated inhibitors. Blot was reprobed for the nuclear protein Ref-1 as a loading control to quantitate enzymatic cleavage. The percentage of cleavage with inhibition was normalized to that with uninhibited enzyme. (d) GzmB induces laminB degradation in isolated nuclei less efficiently than GzmA. The 46-kDa C-terminal fragment after GzmB cleavage (*) is different from the 25-kDa fragment generated by GzmA cleavage (white arrowhead). Serial 4-fold dilutions of GzmA (starting with 200 nM) or GzmB (starting with 310 nM) were added for 2 h. LaminB is fragmented with 3 nM GzmA but requires at least 155 nM GzmB. (e) LaminB cleavage in GzmB-treated nuclei is not enhanced by adding cytosol (1 × 10 7 cell equivalents at highest concentration followed by 4-fold serial dilutions) (Left). The Ser protease inhibitor DCI (lane 1), but not CI (lane 2) or DMSO (lane 3), blocks lamin cleavage by GzmB (Right). GzmB without inhibitors is shown in lane 4 and nuclei without GzmB in lane 5. Blot in a was probed with mAb 101-B7 and b--e with polyclonal laminB Ab.