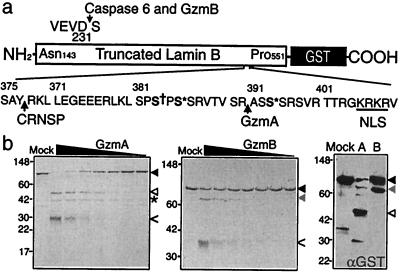
Figure 3.
LaminB-GST is cleaved in vitro by GzmA and GzmB. (a) LaminB (amino acids 143–551)-GST fusion protein was produced in Escherichia coli. Known sites of laminB cleavage by caspases after D231 and by the CRNSP after Y377 are indicated, as are the nuclear localization signal (NLS, underlined), and sites of phosphorylation by p34cdc2 (S† 383) and protein kinase C (S* 385, 395). Figure modified from ref. 39. (b) LaminB-GST protein (1 μg, black arrowhead) was incubated for 1 h at 37°C with 2-fold dilutions of GzmA (Left) or GzmB (Middle) beginning at a highest concentration of 1 μg and analyzed by SDS/PAGE and GelCode stain. Gzm bands are indicated by <. GzmA and GzmB generated cleavage fragments of laminB, indicated by white and gray arrowheads, respectively, were analyzed for N-terminal sequence. The * marks the 42-kDa N-terminal laminB fragment generated by GzmA; the N-terminal GzmB cleavage fragment was not visualized. The sequenced fragments contain the C terminus of the fusion protein because they stain with anti-GST by immunoblot (Right). The GzmA cleavage site is after R392 and the GzmB cleavage site is the known caspase site after D231. GzmA is more efficient than GzmB at cleaving laminB-GST.